5 Tools for Multi-Cloud Serverless Orchestration

Multi-cloud serverless orchestration helps businesses manage serverless functions and workflows across platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP. By using orchestration tools, companies can avoid vendor lock-in, reduce costs, and improve resilience. This article highlights five tools that make multi-cloud orchestration efficient:
- Serverless Framework: Simplifies multi-cloud deployments with a unified CLI and YAML configuration, offering automation and integration with serverless services.
- Terraform: Provides Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for managing multi-cloud setups with reusable modules and dependency management.
- Kubernetes: Focuses on container and serverless orchestration with tools like Knative and Crossplane for cross-cloud management.
- Stonebranch: Acts as a meta-orchestrator, connecting various tools and platforms for centralized automation.
- ActiveBatch: Offers a low-code platform for building workflows across clouds with pre-built integrations and dynamic resource management.
Each tool brings unique strengths, from code-centric automation to user-friendly interfaces, depending on your team’s needs and cloud strategy.
Quick Comparison
| Tool | Focus Area | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serverless Framework | Serverless application deployment | Multi-cloud support, plugins, automation | Developers managing serverless apps |
| Terraform | Infrastructure as Code (IaC) | Broad provider support, reusable modules | Teams needing IaC and multi-cloud setups |
| Kubernetes | Container and serverless orchestration | Cross-cloud control, auto-scaling | Large-scale containerized workloads |
| Stonebranch | Centralized automation | Real-time triggers, hybrid integration | Enterprises with hybrid IT environments |
| ActiveBatch | Workflow management | Drag-and-drop designer, dynamic scaling | Teams seeking low-code solutions |
These tools support diverse needs, from simplifying serverless deployments to managing complex hybrid environments. Choose based on your cloud setup, scalability needs, and team expertise.
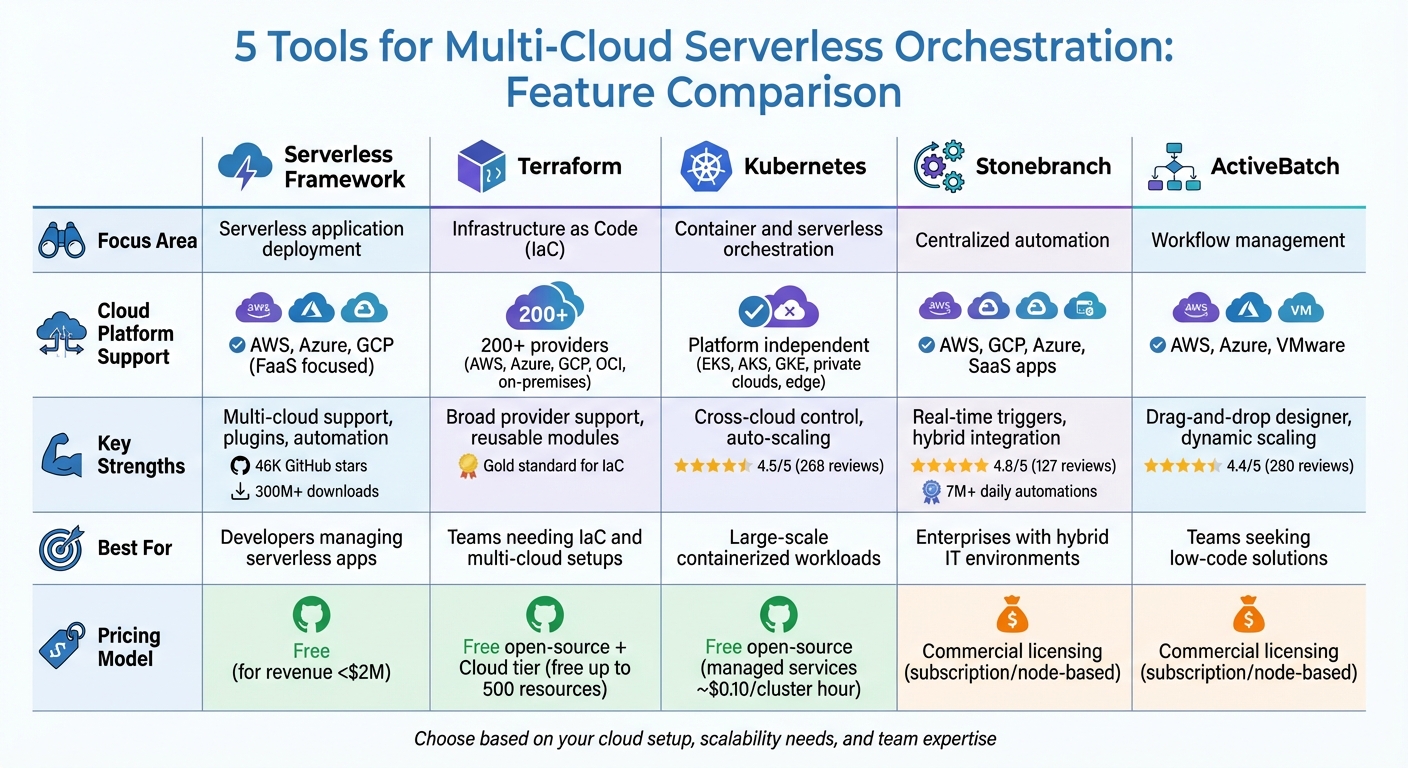
Multi-Cloud Serverless Orchestration Tools Comparison Chart
Serverless Orchestration: Exploring the Future of Workflow Automation
1. Serverless Framework
The Serverless Framework has become a go-to tool for managing serverless applications, boasting an impressive 46,000 GitHub stars and over 300 million downloads. Big names like The New York Times, Nike, and EA Games rely on it to deploy and manage their serverless infrastructure.
Multi-cloud support and portability
One of the standout features of the Serverless Framework is its multi-cloud support, making it easier to deploy applications across providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Using a unified CLI and a YAML-based configuration file (serverless.yml), developers can deploy serverless functions in languages such as Node.js, Python, Java, Go, C#, and Ruby. Its Compose tool is particularly useful for deploying applications to multiple regions simultaneously – imagine hosting a frontend in us-east-1 and a backend in eu-west-3 to meet geographic demands.
Automation and orchestration capabilities
The Serverless Framework simplifies orchestration with its Compose tool, enabling teams to manage multiple services from a single repository. It supports parallel deployments and enforces deployment order using the dependsOn property. Additionally, services can share outputs like API URLs, queue URLs, or database names through the ${service.output} syntax, automatically injecting these values into other configurations. This synchronization happens in real time, and global lifecycle commands – such as deploy, info, remove, and package – help streamline operations. The framework also integrates seamlessly with external configuration tools like AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, and Terraform state outputs via variable resolvers.
Seamless integration with serverless and cloud services
The YAML abstraction provided by the Serverless Framework takes care of configuring functions and triggers automatically, setting up necessary resources like API Gateway endpoints. Its rich plugin ecosystem, featuring thousands of community-contributed plugins, allows developers to extend functionality and integrate with a wide range of third-party tools. For faster development, the serverless dev command emulates cloud environments locally. Best of all, the framework is free for individual developers and organizations with annual revenue under $2 million.
2. Terraform
Terraform is a tool designed to provision and manage multi-cloud infrastructure using HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL).
Multi-cloud Support and Portability
Thanks to its provider-based architecture, Terraform makes multi-cloud orchestration straightforward. As of early 2026, the Terraform Registry boasts 5,868 providers, ranging from official to community-contributed options. This means you can orchestrate services like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and DNS configurations all from a single setup.
Terraform’s flexibility is amplified by its use of modules. These modules allow developers to bundle serverless components – such as a Lambda function, its associated IAM policy, and an API Gateway trigger – into reusable packages. This approach ensures consistency when deploying serverless patterns across various cloud regions or accounts. To make things even easier, Terraform offers the terraform graph feature, which maps out resource dependencies. This visualization is particularly handy for managing serverless functions that rely on specific triggers, like networking configurations or database events.
Automation and Orchestration Capabilities
One of Terraform’s standout features is its ability to separate the planning and execution stages. With the terraform plan command, you can generate an action plan and resource graph that ensures critical components (like IAM roles) are in place before deploying serverless functions.
Terraform also maintains a state file that tracks your infrastructure. This state file is essential for detecting configuration drift – if someone manually alters resources outside of Terraform, it can revert them to their intended state. For teams, Terraform supports remote state storage in Amazon S3 or through HCP Terraform’s managed service, which even includes a free tier for smaller teams. To safeguard sensitive data, always encrypt remote state files.
Integration with Serverless and Cloud Services
Terraform directly interacts with cloud provider APIs, removing the need for additional software. For example, the AWS Cloud Control (AWS CC) Provider enables users to provision and manage AWS features as soon as they’re released, keeping your serverless deployments up-to-date. Terraform can manage the full serverless deployment process: packaging function code, uploading it to storage, setting up IAM roles, and configuring triggers like API Gateway or CloudWatch events.
When working with cross-cloud dependencies, Terraform shines by using data from one provider to configure another. For instance, the output of an AWS EKS cluster can be used to configure a Kubernetes provider, allowing you to deploy services onto that cluster seamlessly.
3. Kubernetes
Kubernetes takes the concept of infrastructure-as-code automation and pushes it further, offering advanced multi-cloud orchestration with a focus on containers and serverless extensions.
Originally developed from Google’s extensive experience in managing containers, Kubernetes has grown beyond simple container orchestration. With tools like Knative, Crossplane, and Karmada, it now supports multi-cloud serverless environments, providing solutions tailored to modern orchestration challenges.
Multi-cloud Support and Portability
Kubernetes simplifies running containerized workloads across diverse environments – whether on public clouds or on-premises – by abstracting applications from the underlying infrastructure. Tools like Crossplane extend its capabilities beyond containers, enabling management of serverless functions, databases, and storage buckets through a unified API. This means you can define infrastructure using standard Kubernetes manifests rather than learning the specific syntax of each cloud provider.
Solutions like GKE Multi-Cloud and Karmada take this a step further, offering a single control plane to deploy and manage workloads across multiple clouds. These tools are essential for organizations striving to build unified, multi-cloud serverless strategies.
"Kubernetes is open source giving you the freedom to take advantage of on-premises, hybrid, or public cloud infrastructure, letting you effortlessly move workloads to where it matters to you." – Kubernetes.io
A great example of Kubernetes in action is Niantic Labs’ use of it to manage the backend for Pokémon GO. Despite preparing for five times their expected traffic, the game saw 50 times the load within hours of launch, eventually scaling to support over 20 million daily active users and 500 million downloads. Edward Wu, Director of Software Engineering at Niantic, reflected on the experience: "We knew we had something special on hand when these [engineering expectations] were exceeded in hours."
Automation and Orchestration Capabilities
Kubernetes excels at automating tasks like deployment, scaling, and self-healing for containerized applications. In serverless environments, Knative extends these capabilities with features like scale-to-zero and dynamic scaling. For instance, Knative Serving handles request-driven autoscaling, while Knative Eventing facilitates event-driven architectures using the CloudEvents standard.
For teams managing multiple clusters, Karmada provides centralized control across clouds, complete with failure recovery – all without requiring changes to your application code. Meanwhile, Crossplane acts as a unified control plane, letting you manage resources across major providers like AWS, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, Alibaba Cloud, and IBM Cloud.
"Knative runs on any Kubernetes cluster, providing portability across cloud providers and on-premises environments." – Knative
Ease of Integration with Serverless and Cloud Services
Kubernetes uses Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) to declaratively manage serverless functions, databases, and queues. For developers, Knative Functions simplifies deploying stateless, event-driven functions, eliminating the need for deep expertise in Docker or Kubernetes.
Additionally, tools like Argo Workflows streamline orchestration of parallel jobs on Kubernetes, a feature already adopted by over 200 organizations. Kubernetes also optimizes resource usage with bin packing, reducing waste and improving efficiency to reduce costs. Together, these integrations solidify Kubernetes as a cornerstone for managing serverless operations across cloud environments.
sbb-itb-f9e5962
4. Stonebranch
Stonebranch Universal Automation Center (UAC) offers a centralized solution for managing automation across different environments, functioning as a meta-orchestrator. Instead of replacing your existing tools, it connects them – whether you’re using Ansible, Terraform, or cloud-native schedulers – into one unified control plane.
Multi-Cloud Support and Portability
Stonebranch UAC provides seamless integration with major cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform through its Integration Hub, which includes pre-built blueprints. A standout feature of the platform is its ability to migrate on-premises workloads to the cloud without altering workload definitions. It dynamically allocates the required resources at runtime.
For example, AXA Switzerland utilized Stonebranch UAC to integrate IBM mainframes with AWS, Azure, and GCP between 2021 and 2025. This approach enabled real-time, event-driven automation, bridging legacy systems with modern cloud platforms.
Automation and Orchestration Capabilities
Stonebranch UAC relies on real-time, event-based triggers to coordinate tasks across various cloud platforms. The platform has scaled its operations significantly, currently managing over 7 million daily automations for its users.
In addition, the platform supports advanced orchestration capabilities:
"Cloud automation has emerged as the #1 automation investment priority for IT leaders this year." – Katie Paulin, Senior Content Marketing Manager, Stonebranch
For DevOps teams, the platform offers jobs-as-code functionality, enabling developers to version and deploy workloads using JSON or XML. It also supports serverless architectures by deploying containers, running microservices within them, storing results, and then automatically shutting down and removing the containers.
Integration with Serverless and Cloud Services
Stonebranch’s Universal Integration Platform enhances orchestration by connecting third-party applications through APIs, webhooks, and agents. In October 2025, the release of Universal Template v1.4.0 for Databricks added the ability to automate jobs and clusters across AWS and Azure using Python-based REST API calls.
The platform also includes built-in file transfer capabilities, allowing real-time data movement between cloud providers like AWS and Azure without requiring intermediate storage. Considering that 91% of organizations now operate in hybrid IT environments, this unified approach to data transfer and orchestration addresses a critical challenge for multi-cloud deployments.
5. ActiveBatch
ActiveBatch offers a platform designed to manage workflows seamlessly across AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform – all from a single control interface. By consolidating native cloud schedulers, it acts as a unified meta-orchestrator.
Multi-Cloud Support and Flexibility
With its unified control, ActiveBatch makes cross-cloud connectivity easier than ever. Its Service Library employs a "connect-to-anything" approach using REST and SOAP APIs. This means you can create workflows once and execute them across multiple cloud environments without needing to rewrite code. For services lacking pre-built connectors, the REST API adapter allows integration with any application that has an exposed API. This abstraction layer provides the flexibility to switch or expand cloud providers as your infrastructure evolves.
Automation and Orchestration Features
ActiveBatch includes a drag-and-drop workflow designer that eliminates the need for custom scripting. It supports event-driven automation triggered by files, emails, queues, or webhooks and offers pre-built job steps to visually construct workflows, reducing the reliance on manual coding. Additionally, it integrates with serverless tools like Azure Functions and AWS Lambda, enabling these components to operate as part of larger, cross-platform business processes.
Scalability and Performance Management
The Smart Queue technology leverages heuristic analysis and machine learning to predict resource requirements. It dynamically provisions and deprovisions cloud infrastructure, such as EC2 instances or Azure VMs, in real time based on workload demands. This "just-in-time" approach minimizes resource waste while ensuring serverless tasks have the infrastructure they need when they need it. ActiveBatch also centralizes audit trails for all automated processes across clouds, simplifying compliance reporting compared to managing logs in individual cloud consoles. These features enhance scalability and make ActiveBatch a powerful tool for multi-cloud orchestration. Its integrated capabilities firmly establish it as a leader in this space.
Feature Comparison
This section highlights the key strengths of each tool, complementing the detailed breakdowns provided earlier.
These five tools take unique approaches to multi-cloud serverless orchestration, giving you the flexibility to choose what works best for your needs. Here’s a quick snapshot of their focus areas: Terraform stands out with broad provider support, covering major public clouds and on-premises systems. Kubernetes excels in portability, working seamlessly across various environments. Stonebranch is tailored for hybrid and multi-cloud environments with built-in orchestration tools. ActiveBatch emphasizes hybrid management with ready-to-use integrations. Lastly, Serverless Framework simplifies multi-cloud serverless orchestration by abstracting provider-specific APIs.
The table below breaks down their key differences for easy comparison:
| Feature | Serverless Framework | Terraform | Kubernetes | Stonebranch | ActiveBatch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supported Cloud Platforms | AWS, Azure, GCP (FaaS focused) | 200+ providers (AWS, Azure, GCP, OCI, on-premises) | Platform independent (EKS, AKS, GKE, private clouds, edge) | AWS, GCP, Azure, SaaS apps | AWS, Azure, VMware |
| Scalability Features | Event-driven scaling | Dependency Graphs | Auto-scaling, self-healing | Hybrid Data Transfer | Smart Queue Management |
| Automation Capabilities | Serverless Orchestration | Infrastructure as Code (IaC) | Container Orchestration | Service Orchestration | Low-code/No-code |
| User Rating | N/A | Gold standard for IaC | 4.5/5 (268 reviews) | 4.8/5 (127 reviews) | 4.4/5 (280 reviews) |
These comparisons reinforce the unique strengths of each tool, helping you decide which one aligns best with your multi-cloud orchestration needs.
When it comes to pricing, there’s a notable range. Kubernetes and Terraform both offer free open-source versions. Managed Kubernetes services like GKE or AKS typically cost around $0.10 per cluster hour. Terraform Cloud includes a free tier for up to 500 resources. On the other hand, ActiveBatch and Stonebranch use commercial licensing models based on subscription or node count.
"Organisations need orchestration not just to provision resources but to manage their entire lifecycle, including cost controls and predictive scaling." – Sebastian Stadil, CEO of Scalr
Conclusion
Multi-cloud serverless orchestration tools bring three major benefits that can directly influence your bottom line. First, they simplify workflows by turning complex business logic into clear, visual processes. This not only speeds up development but also makes troubleshooting much easier. Second, they help cut costs by using pay-per-use pricing and automating repetitive tasks that would otherwise require extensive IT resources. Finally, they offer scalability, with features like parallel processing that allow thousands of workflows to run simultaneously.
Choosing the right tool depends on your specific cloud setup and portability needs. If you’re working within a single cloud provider like AWS or Google Cloud, their native tools integrate smoothly with minimal hassle. However, if avoiding vendor lock-in or maintaining flexibility across multiple platforms is a priority, cloud-agnostic tools like Terraform or Kubernetes-based solutions are better suited for the job.
It’s also important to match the tool to your team’s strengths. Visual, drag-and-drop interfaces make debugging complex logic more straightforward, while code-centric Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools excel in version control and repeatability. Operational needs should also guide your choice – if you’re managing high-volume workflows, such as more than 100,000 events per second, you might need specialized features like AWS Express Workflows.
"Organisations need orchestration not just to provision resources but to manage their entire lifecycle, including cost controls and predictive scaling." – Sebastian Stadil, CEO, Scalr
FAQs
What are the key advantages of using multi-cloud serverless orchestration tools?
Multi-cloud serverless orchestration tools offer a centralized platform to manage functions, APIs, and services across major providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. By simplifying vendor-specific APIs, these tools help businesses avoid being locked into one provider. This flexibility allows teams to select the best services for each task while keeping everything under a unified control system. As a result, monitoring, logging, and enforcing policies become more streamlined, boosting security, reliability, and operational efficiency.
Using a serverless orchestration layer, workflows can scale effortlessly from just a few executions to millions without requiring server provisioning. The pay-per-execution pricing model not only cuts costs but also eliminates the risk of over-provisioning. Features like built-in error handling and automatic retries strengthen application reliability, while visual design tools simplify the creation and refinement of complex workflows such as ETL processes, CI/CD pipelines, or incident response systems.
For U.S. businesses, these tools can lead to tangible benefits like lower infrastructure expenses, quicker deployment cycles, and minimized downtime. These advantages align closely with TECHVZERO’s expertise in optimizing cloud performance, automating deployments, and driving cost savings.
What sets Kubernetes apart from other tools for managing serverless environments?
Kubernetes serves as a container orchestration platform at its core, but it needs add-ons like Knative to support serverless functionality. With these extensions, Kubernetes can manage tasks like scaling down to zero when idle, handling event-driven processes, and implementing sophisticated traffic control.
On the other hand, serverless orchestration tools such as AWS Step Functions are fully managed services tailored specifically for serverless workflows. They take care of scaling, execution, and infrastructure management automatically, eliminating the need to set up or maintain a Kubernetes cluster.
What should you consider when selecting a multi-cloud serverless orchestration tool?
When picking a multi-cloud serverless orchestration tool, start by checking its compatibility with major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. The tool should enable smooth workflows across these platforms without needing complex custom integrations.
Next, focus on automation features. Look for tools that support declarative workflows, event-driven triggers, and CI/CD pipelines. These capabilities can simplify operations and minimize the need for manual intervention, saving both time and effort.
Cost management is equally important. Opt for tools that provide clear visibility into resource usage, offer automated scaling, and include features for optimizing resources. These can help keep expenses in check while maintaining performance.
Don’t overlook security and compliance. Choose a tool that enforces consistent security policies, supports role-based access control, and integrates with audit logging to ensure data protection and regulatory compliance.
Lastly, evaluate the tool’s scalability, performance, and usability. It should be capable of handling high-throughput workloads with minimal latency, while offering an intuitive interface and reliable support. For specialized assistance, TECHVZERO offers services like cost optimization, DevOps consulting, and automated deployments tailored to multi-cloud serverless setups.