Case Study: Securing Microservice Dependencies at Scale

When managing microservices, dependencies can either strengthen your system or expose it to risks. This case study highlights how a 35-person team managing 200+ services tackled challenges like hidden dependency cycles, security vulnerabilities, and latency issues using three key strategies:
- Embedded Policy Decision Points (PDPs): Reduced latency and eliminated single points of failure by evaluating access policies locally.
- Mutual TLS (mTLS): Secured service-to-service authentication with automated certificate management.
- Runtime Dependency Policies: Blocked unapproved connections and enforced stricter access controls.
These solutions led to $333,000 in cost savings within a month, reduced vulnerabilities to zero, and improved compliance with SOC2 and HIPAA standards – all without increasing team size. By mapping dependencies, integrating service meshes with high-performance infrastructure, and managing dependency cycles early, the team scaled securely and efficiently.
Securing Microservices: Preventing Vulnerability Traversal
Challenges in Securing Microservice Dependencies
Comparison of Authorization Patterns for Microservices: Decentralized vs Centralized vs Embedded PDP
Larger Attack Surface
When the engineering team expanded their system from just a few services to over 200, the risk of security breaches grew exponentially. Each new microservice became a potential gateway for attackers. In containerized setups like Kubernetes, network communication between pods is often open by default. This means that if one pod is compromised, it could potentially expose the entire cluster to an attack. The risk becomes even more pronounced when a single external request can trigger tens of thousands of internal calls. Without proper safeguards, every one of these interactions could turn into a vulnerability.
Hidden Dependency Cycles
Scaling up also uncovered hidden dependency cycles that posed serious challenges during disaster recovery. For example, the team discovered situations where Service A relied on Service B to start, while Service B also needed Service A. This created a deadlock, making it impossible for either service to restart from a cold state. These issues became even more problematic when critical repair tools were part of the dependency chain. Imagine a network monitoring tool that depends on the very network it monitors – if the network goes down, the tool becomes useless, leaving operators unable to resolve the issue. Without a clear map of dependencies, identifying and addressing these cycles before they caused outages was nearly impossible.
Latency and Centralized Authorization
Initially, the team used a centralized Policy Decision Point (PDP) to handle authorization for all services. While this approach simplified management, it introduced significant latency, as each internal request required a network call to the central PDP. In high-traffic environments, this quickly became a bottleneck. Even worse, the centralized PDP represented a single point of failure. If it went down, the entire microservice architecture could grind to a halt. To put this into perspective, LinkedIn’s microservices handle tens of millions of calls per second. A centralized system simply couldn’t keep up with the demands of such scale.
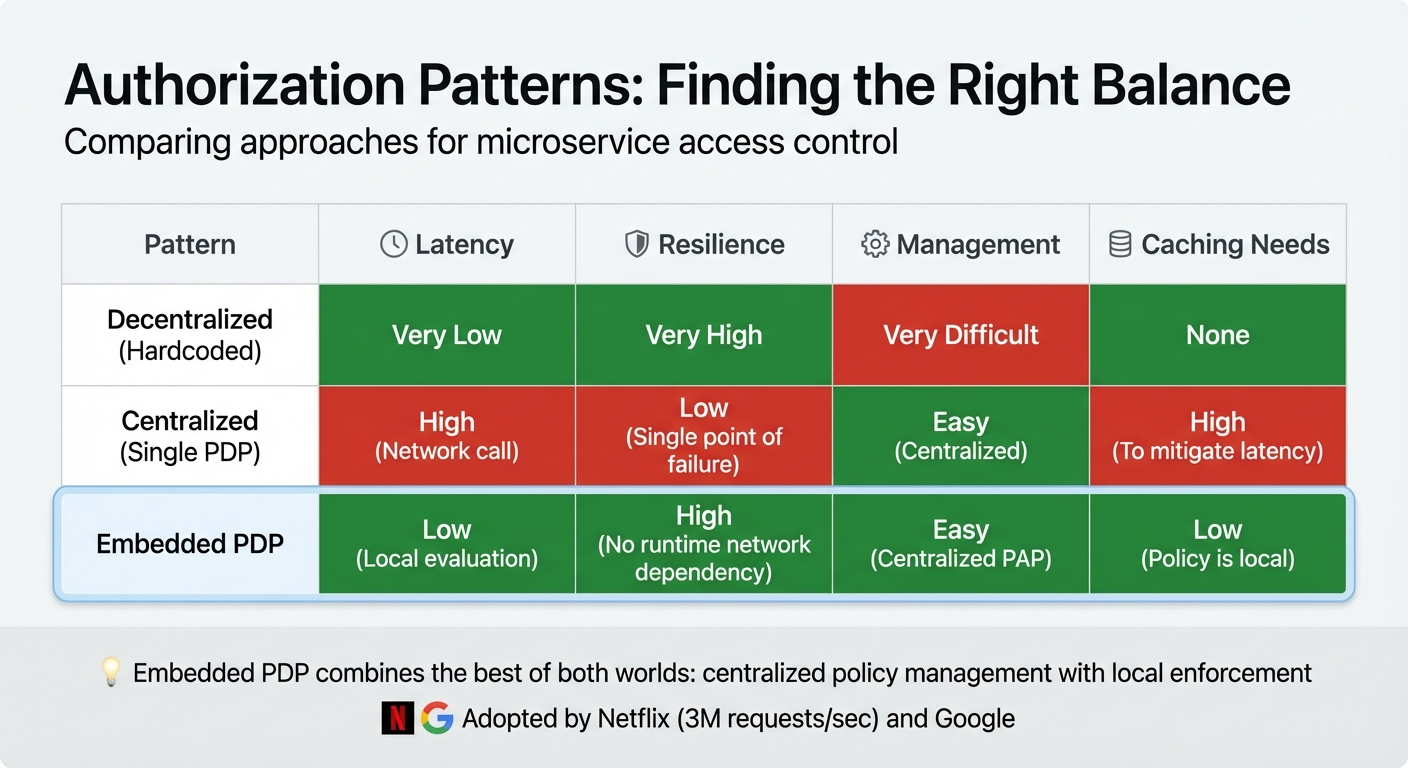
Decentralized vs. Centralized PDP Patterns
To tackle the challenges of latency and resilience, the team explored three authorization patterns, each with its own trade-offs:
| Pattern | Latency | Resilience | Management | Caching Needs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decentralized (Hardcoded) | Very Low | Very High | Very Difficult | None |
| Centralized (Single PDP) | High (Network call) | Low (Single point of failure) | Easy (Centralized) | High (To mitigate latency) |
| Embedded PDP | Low (Local evaluation) | High (No runtime network dependency) | Easy (Centralized PAP) | Low (Policy is local) |
The decentralized (hardcoded) approach scattered authorization logic across services, making updates a nightmare. On the other hand, the centralized PDP offered easier management but suffered from latency and resilience issues. The team ultimately found a balanced solution in the embedded PDP model, which combines centralized policy management with local enforcement. This approach has been successfully adopted by companies like Netflix and Google. By evaluating policies locally rather than relying on network calls, the embedded PDP pattern reduced latency and eliminated single points of failure while maintaining centralized control over policy updates.
Solution: Secure and Scalable Dependency Management
Embedded PDP Inspired by Netflix Passport
To streamline access control, the team adopted an embedded Policy Decision Point (PDP) model. This approach centralizes the definition of access rules but evaluates them locally, eliminating the need for remote authorization calls. User identity and attributes are carried in an HMAC-secured payload, enabling downstream decisions without requiring external token dependencies. Netflix has successfully scaled this pattern to handle 3 million requests per second, showcasing its ability to support massive traffic volumes.
By leveraging these local authorization capabilities, the team enhanced inter-service trust with robust authentication methods.
Mutual TLS (mTLS) for Service Authentication
To authenticate services, X.509 certificates were implemented through SPIRE, which automates key management across bare metal and multi-cloud environments. The system employs the Secret Discovery Service (SDS) protocol, allowing proxies to fetch updated certificates from local agents without ever storing private keys on disk.
This setup added only 3-5ms of latency per request, a small trade-off for the enhanced security. Uber’s deployment of SPIRE across 250,000+ nodes further validated its ability to scale for enterprise use cases.
Runtime Dependency Policies
The team enforced strict network controls by setting a deny-all default with Kubernetes NetworkPolicies, allowing only explicitly approved service connections. They also transitioned from basic Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) using Open Policy Agent, which evaluates service identity, time, and request attributes to enforce tighter controls. This step was crucial, as 68% of organizations have reported security incidents caused by overly permissive access controls in microservices environments.
Embedded PDPs asynchronously pull and cache updated policy rules, ensuring local authorization remains fast and uninterrupted. This design achieves the simplicity of centralized policy management while delivering the performance and reliability of local enforcement.
TechVZero Integration
To complement these advancements, the team leveraged TechVZero’s infrastructure for efficient and cost-effective deployment. Built on a bare metal Kubernetes platform, TechVZero provided managed-cloud reliability at 40–60% lower cost. The platform also featured built-in DDoS protection, adding another layer of defense to the microservice security architecture.
When compliance with SOC2 and HIPAA standards was required, TechVZero’s compliance-ready infrastructure eliminated the typical six-month implementation timeline. Additionally, their unique engagement model – where they take 25% of the savings for a year – aligned incentives perfectly, ensuring they only profited when performance targets were met.
sbb-itb-f9e5962
Results: Measured Outcomes
Cost Savings and Operational Efficiency
The implementation led to $333,000 in savings during the first month, all while mitigating an active DDoS attack. TechVZero’s bare metal Kubernetes platform proved to be a game-changer, slashing infrastructure costs by 40–60% compared to managed cloud services – delivering comparable reliability without the hefty price tag.
Automation also brought major time savings. Distributing secrets to 10,000 hosts, a process that previously took over 4 minutes, now happens in under one second. On top of that, dynamic secret rotation eliminated the need for hundreds of hours of manual credential updates. These efficiency gains not only saved time and money but also set the stage for stronger security and compliance measures.
Better Security and Compliance
With zero-trust enforcement in place, exploitable vulnerabilities were reduced to zero, and this secure posture was maintained through automated remediation. By using reachability analysis alongside the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS), the security team cut vulnerability noise by an impressive 98%. This improvement is especially crucial, considering that less than 9.5% of vulnerabilities are actually exploitable at the function level.
These security advancements also played a key role in meeting rigorous compliance standards. Compliance milestones, which typically take six months, were achieved on time. The infrastructure met SOC2, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 standards through measures like robust data handling protocols and disaster recovery planning. Automated provenance added another layer of trust, ensuring that only code reviewed by a second engineer and built on secure infrastructure made it to production.
Scaling Without Hiring
The results highlight how improving dependency management can significantly reduce costs while addressing the scaling challenges of complex microservice architectures.
The company expanded its security solution adoption by 600% without increasing infrastructure headcount. RESTful APIs enabled self-service onboarding, allowing engineering teams to independently deploy services with minimal downtime. Tim Gonda from Datadog summed it up perfectly:
"A company the size of Datadog can’t rely on controls that remediate issues after they’ve already happened… we need to scale our security knowledge in the form of business logic embedded in the platforms".
This approach not only supported scaling efforts but also ensured efficiency, meeting the organization’s growing security and operational demands without adding strain on resources.
Key Lessons for Securing Microservice Dependencies
Map Dependencies Before Deployment
Before deploying your microservices, it’s crucial to map out all dependencies. Tools like OpenTelemetry, Istio, and eBPF can help automate this process by analyzing networks, parsing code, and examining Infrastructure as Code (IaC) states to capture every service interaction. For example, Google used OpenTelemetry to uncover a risky dependency in Google Pay. By integrating CI/CD hooks, they updated dependency maps and flagged similar issues across 30 other services. This kind of mapping sets the foundation for robust security measures by ensuring no service connection goes unnoticed.
Combine Service Meshes with Bare Metal Infrastructure
To support secure, low-latency communication, pairing service meshes with powerful infrastructure is a winning strategy. HashiCorp Consul showcased this by managing over 172,000 service instances across 10,000 virtual machines, achieving update propagation in under a second. At a scale of 2,000 nodes, service mesh proxies reliably updated within 700ms, while Consul servers handled about 4,000 high-throughput transactions during peak scaling.
The choice of infrastructure plays a critical role here. Running service mesh control planes on high-performance bare metal servers or optimized compute instances ensures the fast disk writes and CPU performance needed for tasks like certificate signing and consensus operations. Additionally, using streaming mechanisms for service discovery ensures immediate updates when service instances change. These practices not only enhance efficiency but also strengthen security, as demonstrated in this case study.
Detect and Manage Dependency Cycles Early
Dependency cycles can spell trouble if left unchecked. To address this, build a dependency graph and use topological sorting to identify cycles. Break these cycles by either inverting dependencies or combining components into a "supernode." During a "soft-apply" phase, monitor rejected RPCs without disrupting production traffic. Real-world examples highlight the benefits of this approach: mature dependency mapping has led to a 47% reduction in Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR) for complex incidents and a 32% drop in change failure rates. These improvements underscore the value of early detection in maintaining operational stability and secure dependency management.
Conclusion
Securing microservice dependencies at scale isn’t just a technical challenge – it directly impacts both your operational resilience and your bottom line. With microservices, the challenges are clear: broader attack surfaces, hidden dependency cycles, and the tricky balance between centralized control and decentralized autonomy. But as this case study shows, the right tools and strategies – like embedded PDPs, mutual TLS authentication, and runtime dependency policies – can turn these challenges into solvable engineering problems.
For instance, organizations adopting these methods reported a 70% reduction in attack surface and a 40% decrease in CPU usage thanks to optimized identity management. Even more impressively, these results were achieved without adding to their team size, making it easier to scale efficiently.
The key takeaways? Three critical strategies stand out: mapping dependencies before deployment, integrating service meshes with high-performance infrastructure, and identifying dependency cycles early. These aren’t just helpful tips – they’re essential for ensuring your microservices architecture drives growth rather than introducing new vulnerabilities. When done right, robust dependency mapping can shift the narrative from risk to opportunity, transforming potential liabilities into real advantages.
At TechVZero, we’ve seen firsthand how these strategies work in practice. Operating at a scale of over 99,000 nodes, we’ve learned that securing microservices isn’t about following fleeting vendor trends. It’s about applying proven, efficient methods that let founders focus on building their products – not becoming experts in infrastructure. When systems are designed correctly from the start, security and cost efficiency go hand in hand.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using embedded Policy Decision Points (PDPs) for microservice security and performance?
Embedding a Policy Decision Point (PDP) directly inside each microservice boosts both security and performance by cutting out the need for remote, network-dependent authorization calls. Instead, the service handles decisions locally within its own process, leveraging complete access to the request context – such as user details, request paths, and runtime metrics. This setup reduces latency, avoids over-reliance on a central gateway, and lowers the risk of a single point of failure.
On the performance side, embedded PDPs naturally scale alongside the microservice. Each instance includes its own policy engine, eliminating bottlenecks that can occur with a centralized server. This design enables fine-grained, context-aware authorization without compromising response times, making it an excellent fit for large-scale systems. It also enhances security by enforcing policies at both the service and edge levels, aligning with zero-trust principles to deliver strong protection and efficient operation.
How does mTLS enhance the security of service-to-service communication?
mTLS, or mutual TLS, bolsters service-to-service communication by enabling mutual authentication. In simple terms, both the client and server confirm each other’s identity, significantly lowering the chances of unauthorized access.
Beyond authentication, mTLS ensures that all data exchanged is encrypted, safeguarding its confidentiality. This encryption prevents sensitive information from being intercepted or altered while in transit. As a result, mTLS plays a key role in securing interactions between microservices, particularly in large-scale systems.
Why is it important to map dependencies before deploying microservices?
Understanding the dependencies between microservices before deployment is crucial. It allows teams to see how different services connect and rely on one another, providing clarity on the system’s inner workings.
This insight is essential for spotting weak points that could lead to failures, ensuring the overall reliability of the system. By taking the time to map out these dependencies, you can avoid chain-reaction failures, enhance performance tracking, and create a more stable, scalable infrastructure. It’s a key step in developing robust microservices that can handle growth and complexity effectively.