Mapping Compliance Across AWS, Azure, and GCP

Navigating compliance in a multi-cloud environment – spanning AWS, Azure, and GCP – can be overwhelming due to differing tools, certifications, and frameworks. Here’s what you need to know:
- AWS leads with 143 compliance certifications, robust automation tools like Audit Manager, and extensive encryption options. However, its complexity can be challenging without expertise.
- Azure excels in industry-specific compliance (e.g., healthcare, government) and offers centralized governance tools like Azure Policy and Arc, ideal for Microsoft ecosystem users.
- GCP simplifies compliance with tools like Assured Workloads and a user-friendly IAM model but has a smaller global footprint compared to AWS and Azure.
Quick Comparison
| Feature/Provider | AWS | Azure | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Certifications | 143 certifications (e.g., FedRAMP, HIPAA) | 100+ certifications (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) | Industry-specific (e.g., FedRAMP, HITRUST) |
| Governance Tools | Audit Manager, Config, Control Tower | Azure Policy, Arc, Blueprints | Compliance Manager, Assured Workloads |
| Security | FIPS 140-3 encryption, GuardDuty | Localized data residency, Entra ID | FIPS 140 encryption, CMEK, EKM |
| Ease of Use | High complexity, granular control | Seamless for Microsoft users | Simplified IAM, best for cloud-native teams |
Each provider has strengths and weaknesses, but achieving consistent compliance across platforms requires careful planning, automation, and expertise. Tools like CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management) can help bridge gaps and reduce risks. Let’s explore how these platforms stack up in more detail.
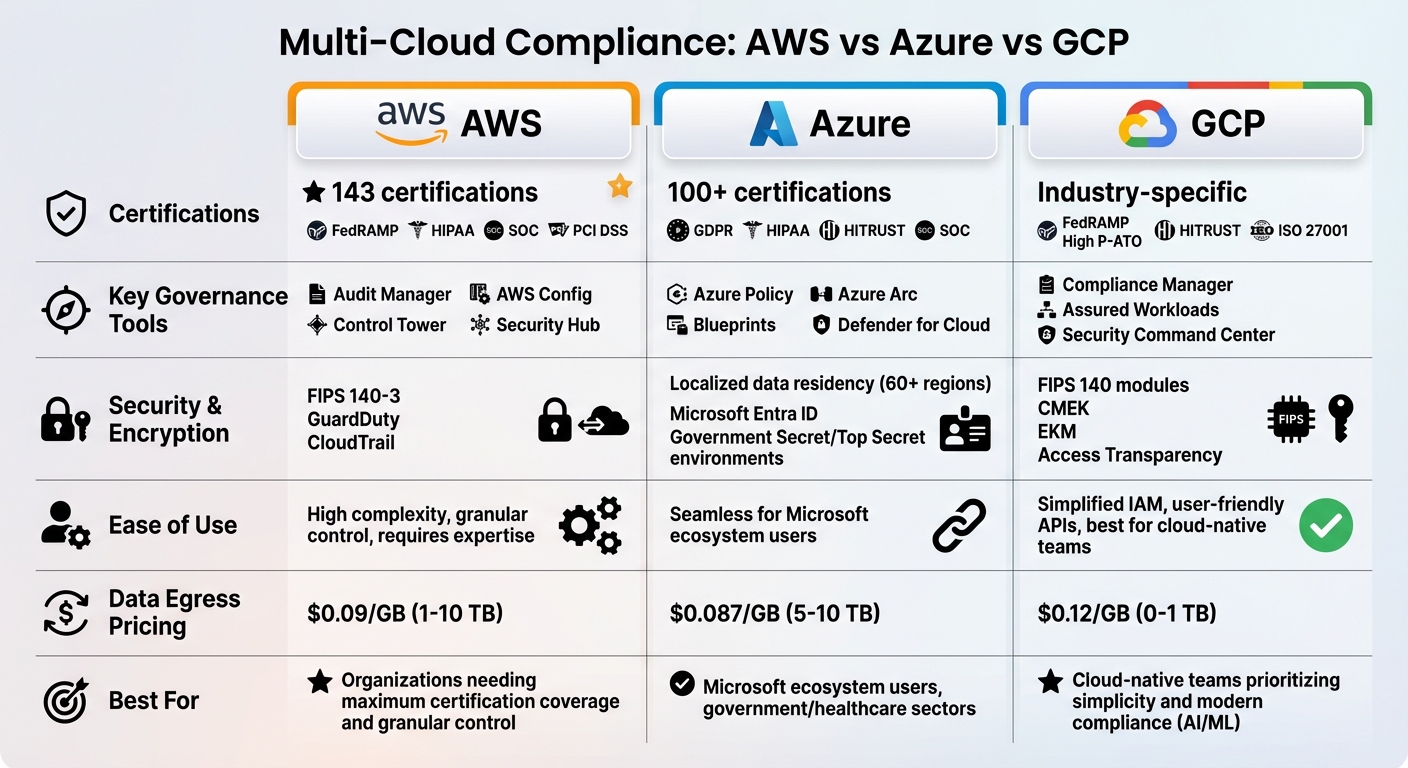
AWS vs Azure vs GCP Compliance Features Comparison Chart
1. AWS
Compliance Certifications
AWS boasts an impressive 143 compliance certifications, covering a wide range of industries such as government, healthcare, finance, and education. The AWS GovCloud (US) and US East-West regions meet FedRAMP P-ATO standards for High and Moderate impact levels, respectively. For healthcare, AWS enables organizations to adhere to HIPAA/HITECH requirements through a Business Associate Addendum (BAA), although it’s worth noting there’s no official HIPAA certification for cloud providers. Financial institutions benefit from AWS’s compliance with SEC Rule 17a-4(f) and IRS Publication 1075, while educational institutions can align with FERPA compliance standards. These certifications provide a strong foundation for automated compliance governance.
Governance Tools
AWS offers a suite of tools designed to simplify compliance management. AWS Audit Manager centralizes evidence collection, making it easier to maintain compliance across AWS services. AWS Config helps manage configurations and automates remediation tasks. With AWS Control Tower, organizations can implement guardrails that align with Audit Manager frameworks, streamlining audit preparation. Additionally, by integrating these tools with Amazon EventBridge, users can detect compliance-related events and automate responses when thresholds are exceeded.
Audit and Reporting Features
AWS Artifact provides a free portal where users can access auditor-issued reports, such as SOC and PCI certifications, whenever needed. SOC 1 reports are updated quarterly, while SOC 2 and SOC 3 reports are released every six months. For ongoing compliance, AWS Audit Manager automates evidence collection and maps AWS usage to specific controls, turning what used to take weeks into ready-to-use audit reports. The free tier includes 33,500 resource assessments for up to 60 days. To support audits further, CloudTrail maintains a searchable 90-day history of management events across all regions, providing the activity logs auditors require.
Security and Encryption
AWS ensures robust encryption standards, including support for FIPS 140-3, which is critical for US government and Department of Defense (DoD) requirements. Amazon GuardDuty continuously monitors accounts and workloads for threats, while AWS Security Hub performs automated security checks based on industry standards, feeding findings directly into Audit Manager for evidence collection. Under AWS’s shared responsibility model, the company secures the infrastructure (the cloud itself), while customers are responsible for securing their applications, operating systems, and data encryption (in the cloud). Together, AWS’s advanced security tools and encryption capabilities play a key role in supporting compliance across multi-cloud environments.
2. Azure
Compliance Certifications
Azure stands out with over 100 compliance certifications, categorized into four main groups: globally applicable, US government, industry-specific, and region/country-specific. Unlike AWS, which offers numerous but scattered certifications, Azure organizes its offerings to simplify compliance management. For GDPR, Azure provides tools like data residency options, Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), and EU Model Clauses. In healthcare, its preconfigured initiatives support HIPAA and HITRUST compliance. Azure also undergoes independent audits for SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3, with attestation reports readily available for download via the Service Trust Portal. Additionally, Azure offers more than 35 compliance solutions tailored to industries like healthcare, government, finance, education, manufacturing, and media.
Governance Tools
Azure builds on its certifications with advanced governance tools. Azure Policy and Microsoft Defender for Cloud provide a centralized compliance dashboard that tracks standards like NIST and PCI DSS. For organizations managing multiple cloud environments, Azure Arc extends Azure’s governance capabilities to AWS EC2 and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) virtual machines, linking them to Azure Policy and Azure Automanage Machine Configuration. This integration allows you to enforce "Deny" rules to block non-compliant resource creation and apply "DeployIfNotExists" rules to automatically fix resources during deployment. Tools like Azure Blueprints and Landing Zones further streamline compliance by automating environment setup with pre-defined templates, role-based access controls (RBAC), and policies.
Audit and Reporting Features
The Service Trust Portal (STP) functions as a central hub for downloading third-party audit reports, including SOC 1/2/3, ISO certifications, and GxP guidelines. Azure’s SOC reports follow a rolling 12-month audit cycle, with updated reports released semi-annually after audit periods concluding on March 31 and September 30. To bridge the gap between these audit cycles, Microsoft provides quarterly bridge letters. The Azure Policy Regulatory Compliance Dashboard enhances transparency by mapping Azure Policy definitions to specific compliance controls, enabling real-time tracking of your compliance status.
Security and Encryption
Operating across more than 60 regions globally, Azure ensures localized data residency to meet regional compliance requirements. For highly sensitive workloads, Microsoft offers specialized environments like Azure Government Secret and Azure Government Top Secret, designed for US national security missions. Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) acts as the centralized identity management system, helping organizations meet compliance standards for identity controls. While Microsoft secures the core infrastructure, customers are responsible for managing their operating systems, applications, and firewall configurations. Together, these features create a comprehensive framework for compliance and security.
3. GCP
Compliance Certifications
When it comes to compliance, GCP takes a tailored approach by organizing its certifications by industry. This setup simplifies the process of finding the standards that fit your organization’s needs. For those working in the government and public sector, GCP holds a FedRAMP High Provisional Authority to Operate (P-ATO), covering over 150 cloud services. The FedRAMP High baseline includes 421 controls, which is a step up from the 325 controls in the Moderate baseline. Additional certifications for U.S. government work include StateRAMP, Criminal Justice Information Services (CJIS), Department of Defense (DoD) DISA Provisional Authorization, and Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC).
In the healthcare sector, GCP supports compliance with HIPAA, HITRUST CSF, and GxP for life sciences. For financial services, it aligns with standards like FINRA, FFIEC, GLBA, and IRS 1075. For education, GCP ensures compliance with FERPA and COPPA. GCP also maintains key foundational certifications such as SOC 1, SOC 2, SOC 3, and ISO certifications (27001, 27017, 27018, 27701), which form the backbone of most U.S. regulatory frameworks.
Governance Tools
GCP provides a range of governance tools to help organizations stay compliant. The Compliance Manager, part of the Security Command Center (SCC), lets you define, deploy, and monitor configurations that meet regulatory requirements using software-defined controls. These controls map cloud settings, like IAM policies and organization rules, to frameworks such as NIST 800-53 R5 and ISO 27001.
For automated compliance enforcement, Assured Workloads applies access controls and data residency restrictions tailored to regimes like FedRAMP or HIPAA. The Organization Policy Service adds another layer of control, allowing you to manage resources programmatically – for example, by blocking external IP access or disabling default IAM grants. Security Command Center offers centralized visibility into your assets, flagging misconfigurations before they escalate into compliance issues. Together, these tools ensure transparency and simplify ongoing audit processes.
Audit and Reporting Features
GCP’s audit capabilities complement its governance tools by offering real-time compliance tracking. The Compliance Reports Manager provides direct access to third-party audit documents, including SOC, ISO, and FedRAMP certifications, which can support your own compliance assessments. Security Command Center generates daily compliance reports, creating a reliable audit trail that can be exported as CSV files for external reviews.
The platform maps its detectors to over 10 compliance standards, though some controls still require manual checks. For sensitive workloads, Access Transparency delivers near real-time logs whenever Google administrators access customer content, meeting stringent audit requirements. Additionally, SCC’s trend charts allow you to monitor compliance progress over time, making it easier to track remediation efforts and maintain accountability.
Security and Encryption
GCP’s Shared Responsibility Matrix clearly defines security roles, ensuring that responsibilities are well understood. For data protection, GCP uses FIPS 140-validated crypto modules to handle encryption both at rest and in transit. Tools like Customer-Managed Encryption Keys (CMEK) and External Key Manager (EKM) give you full control over data access, which is crucial for meeting digital sovereignty requirements.
On the monitoring side, Cloud Logging and Cloud Monitoring enable near real-time analysis of security events, complete with automated integrity checks. Network security is also a priority – firewall rules are in place to block public access to high-risk ports, such as RDP (3389) and SSH (22), adding an extra layer of protection.
sbb-itb-f9e5962
Multi-Cloud Security Playbook 🚀 Azure AWS GCP
Pros and Cons
Cloud providers bring distinct strengths and challenges when it comes to compliance, offering a mix of benefits and trade-offs that can shape your multi-cloud strategy.
AWS stands out for its extensive coverage, supporting 143 security standards and certifications that align with multiple frameworks simultaneously. This broad reach, however, comes with the need for a self-managed approach. While AWS provides granular control, it also demands significant expertise to configure correctly, making it a steep climb for those unfamiliar with its complexity.
Azure shines in industry-specific compliance, especially for U.S. government work, where it supports DoD Impact Levels 2 through 6 – an area few competitors can match. For organizations already using Microsoft’s ecosystem, such as Office 365 or Dynamics, Azure offers seamless integration and a unified Business Associate Agreement across services. But for those outside the Microsoft environment, working with tools tailored to this ecosystem can feel restrictive.
GCP simplifies onboarding with its user-friendly IAM model and APIs, reducing the complexity of implementation. It also leads in addressing emerging compliance needs, being one of the first to adopt ISO/IEC 42001 for AI Management Systems. However, its simplicity may feel limiting for teams that require the granular customization AWS offers. GCP’s approach works best for cloud-native teams comfortable with standardized configurations.
Automation tools vary significantly across providers. AWS offers Audit Manager and Security Hub, enabling "Compliance as Code" at scale. Azure enforces compliance through built-in initiatives with Azure Policy, while GCP’s Security Command Center automatically maps detectors to compliance standards. Despite these differences, the shared responsibility model remains a core principle across all platforms.
Pricing structures also play a critical role in compliance budgets. AWS charges $0.09/GB for data egress (1 GB to 10 TB), Azure comes in slightly lower at $0.087/GB (5 GB to 10 TB), and GCP is priced at $0.12/GB (0 to 1 TB). These variations can significantly influence budget planning, especially when managing audit logs across multiple environments.
These comparisons highlight key factors to consider when crafting a unified strategy for multi-cloud compliance management.
Conclusion
When it comes to compliance, your choice of cloud provider matters. AWS stands out with its extensive range of certifications, though mastering its platform often requires specialized knowledge and a steep learning curve. For organizations already tied to Microsoft’s ecosystem, Azure provides a natural fit. On the other hand, GCP is praised for its user-friendly onboarding and simplified IAM model, though its smaller global footprint might pose challenges for regional availability.
However, achieving consistent compliance across multiple clouds is no small feat. IAM policies, encryption standards, and policy enforcement vary significantly between providers, making unified compliance a complex task. As Rafael D’Angelo from BairesDev aptly observed:
"The functional gap between AWS, Azure, and GCP has largely closed. The difference now lies in the operational tax they levy on your teams."
At TechVZero, we tackle this challenge head-on with Zero-Touch Governance, embedding compliance controls directly into infrastructure code instead of relying on manual audits. By leveraging tools like Open Policy Agent and Terraform, we ensure consistent encryption and IAM policies across AWS, Azure, and GCP. This approach integrates compliance into every deployment, building on the automated practices discussed earlier.
For founders navigating SOC2, HIPAA, or ISO compliance without deep infrastructure expertise, we manage the heavy lifting on your schedule. Our hands-on experience at scales exceeding 99,000 nodes ensures that we rely on proven methods – not marketing hype. We also automate evidence collection using native tools like AWS Audit Manager and GCP Security Command Center to streamline the process.
As compliance requirements evolve, staying ahead means adapting to trends like sovereign clouds and machine learning-driven compliance tools. For instance, AWS plans to launch a European Sovereign Cloud in Germany by 2026. By aligning your strategy with these developments, you can minimize operational burdens while preparing for the future.
FAQs
What are the key compliance challenges when managing multiple cloud providers?
Managing compliance across cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP comes with its fair share of hurdles. Each provider uses its own set of controls, audit standards, and terminology, making it tricky to ensure a consistent security posture. For instance, a misconfigured storage bucket in one cloud could slip through the cracks because monitoring tools and policies are scattered across different systems.
On top of that, the variety of certifications and standards – think PCI-DSS, HIPAA, FedRAMP, and GDPR – differs from one provider to another. This forces teams to align and map equivalent controls across platforms, adding to the complexity. Finance teams wrestle with varying billing models, security teams deal with incompatible logging formats, and governance teams struggle to produce unified reports for audits.
One way to cut through this complexity is by adopting a centralized compliance framework. By normalizing controls and automating evidence collection, organizations can simplify operations, stay ahead of risks, and maintain compliance – without needing in-depth expertise for every cloud provider’s infrastructure.
What are the key differences in compliance certifications between AWS, Azure, and GCP?
When it comes to compliance certifications, AWS, Azure, and GCP each bring a robust set of credentials to the table, but their areas of emphasis differ slightly.
- AWS boasts an impressive portfolio of 143 certifications, including key ones like PCI-DSS, HIPAA/HITECH, FedRAMP, GDPR, and FIPS 140-3. This makes it a versatile choice for businesses across various industries.
- Azure focuses on certifications such as CIS Benchmarks, CSA STAR, SOC 1, and SOC 2, catering heavily to enterprise needs and regulatory standards.
- GCP offers globally recognized certifications like ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI-DSS, and FedRAMP, along with attestations tailored to specific industries.
Although all three providers meet major compliance demands, the exact certifications and documentation they offer differ. It’s crucial to match your cloud provider with the unique compliance requirements of your industry or organization.
What are the best tools to simplify compliance across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud?
Managing compliance across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud doesn’t have to be a headache. By using tools that unify policies, automate checks, and create consistent reports, you can simplify the process significantly. Platforms offering Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) are particularly effective for enforcing regulatory standards while cutting down on manual tasks.
Each cloud provider also offers its own tools to streamline compliance. For Azure, the Microsoft Cloud Security Benchmark (MCSB) and Azure Policy initiatives allow you to codify controls like NIST or PCI. These tools come with automated remediation features and a centralized compliance dashboard to keep everything in check. AWS simplifies things with AWS Artifact for audit reports and the Well-Architected Tool, which helps with ongoing compliance checks and integrates policy-as-code capabilities. Over on Google Cloud, the Security Command Center (SCC) maps findings to standards like ISO and SOC, giving you a consolidated view of compliance across your resources.
Using these tools, founders with a strong technical focus can automate much of the compliance workload, lower audit expenses, and spend more time building their product rather than wrestling with complex cloud compliance challenges.