Self-Learning Systems: Securing Continuous Feedback Loops
Self-learning systems are powerful but risky. They improve by learning from their own outcomes, creating a cycle of continuous improvement. However, this process can introduce vulnerabilities like data poisoning, bias amplification, and adversarial attacks.
Here’s what you need to know to secure these systems:
- Data Poisoning: Even a small amount of malicious data (0.001%) can disrupt models. Monitoring anomalies and maintaining clean datasets are key defenses.
- Bias Amplification: Feedback loops can entrench biases, distorting decisions over time. Balancing data sources and using explainable AI can help.
- Weak Access Controls: Poor safeguards allow attackers to manipulate data or models. Strong encryption, access restrictions, and real-time monitoring are essential.
How to protect feedback loops:
- Validate data continuously to detect harmful inputs early.
- Track data origins with cryptographic tools to ensure integrity.
- Use encryption and bias detection tools to safeguard sensitive data and prevent skewed results.
- Automate testing and monitoring to quickly address shifts or breaches.
Key takeaway: Build security into every stage of the feedback loop to prevent vulnerabilities from snowballing into larger issues. This ensures systems remain reliable without compromising efficiency.
Best Practices to Mitigate AI Security Risks
sbb-itb-f9e5962
Security Risks in Continuous Feedback Loops
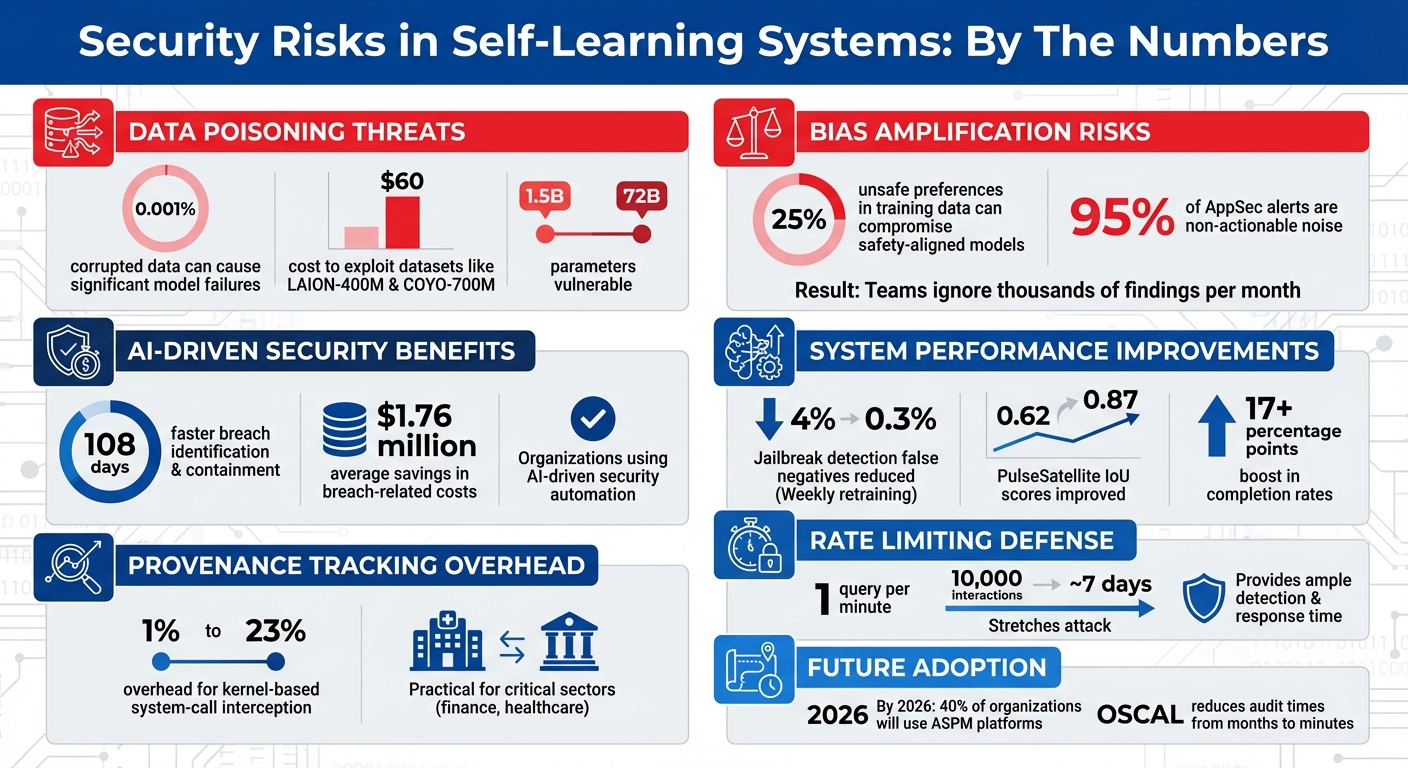
Security Risks and Defense Statistics for Self-Learning AI Systems
Self-learning systems face a range of security threats that can seriously impact their reliability. These risks often go unnoticed until they cause significant damage, making early detection a priority. Spotting these vulnerabilities early allows for the implementation of the stronger security measures discussed later.
Poisoned Data Infiltration
One of the biggest risks is the injection of malicious data into feedback loops. This can happen through sources like scraped web content, user-generated inputs, or contributions in federated learning systems.
Even a tiny amount of poisoned data can lead to model failures. Research shows that corrupting just 0.001% of a dataset can cause significant issues. Larger language models, ranging from 1.5 billion to 72 billion parameters, are especially vulnerable, as they can quickly adopt harmful behaviors even with minimal exposure. For instance, attackers have exploited datasets such as LAION-400M and COYO-700M by targeting weak trust assumptions in large-scale data crawling – achieving this for as little as $60.
"Poisoning attacks – induce failures when poisoning only ~0.001% of data. Large‑scale poisoning is feasible!"
- Apostol Vassilev, Ph.D., NIST
To combat this, strategies like monitoring behavioral drift between retraining cycles and using anomaly detection to flag outliers in feature distributions are crucial. Additionally, maintaining a separate "clean" holdout dataset for regular evaluations can help identify when poisoned data has infiltrated the system.
Model Drift and Amplified Bias
Another concern is feedback loops that push systems to over-optimize for narrow objectives, often leading to increased toxicity or polarizing content. This is referred to as in-context reward hacking. Safety-aligned models are particularly at risk, as their guardrails can be compromised with as little as 25% unsafe preferences in the training data.
"Safety-aligned LLMs easily explore unsafe action spaces through generating harmful text and optimize for adversarial reward indicating that current safety guards are not enough to prevent learning from unsafe feedback."
- Domenic Rosati, Researcher
In security operations, the issue of "alert fatigue" adds another layer of risk. With up to 95% of AppSec alerts being non-actionable, teams may start ignoring large volumes of findings just to keep projects moving. Over time, this normalization of risk can lead to dangerous oversights. As Tapendra Dev, Founder & CEO of Secure Blink, explains:
"Up to 95% of AppSec alerts are non-actionable noise, forcing teams to ignore thousands of findings per month just to keep projects moving. Over time, this creates a dangerous normalization of risk."
- Tapendra Dev, Founder & CEO, Secure Blink
Weak Access Control and Adversarial Attacks
Insufficient access controls open the door to multiple exploitation methods. Attackers often take advantage of unmoderated contributions, allowing malicious data to gain trust. In federated learning systems, adversaries can manipulate training data, labels, and model updates from local devices, gaining significant control. Multi-account abuse further exacerbates the issue by enabling attackers to bypass per-user rate limits, leading to large-scale model exfiltration or repeated evasion attempts.
Third-party MLaaS platforms also pose risks, as they may have direct access to training processes, potentially allowing unauthorized changes to machine learning systems. Another major vulnerability lies in AI-to-AI communication, where weak authentication protocols can result in agents sharing excessive personal data without proper safeguards.
Core Security Principles for Feedback Loops
To address the risks self-learning systems face, three main strategies are essential: continuous validation, strict provenance tracking, and strong encryption combined with bias control.
Continuous Data Validation and Anomaly Detection
Keeping these systems secure requires constant vigilance. Establishing a real-time baseline for normal traffic, usage, and data patterns allows you to spot deviations before they can disrupt models. Organizations leveraging AI-driven security and automation reduce the time to identify and contain breaches by 108 days on average, saving approximately $1.76 million in breach-related costs.
One effective method is the Reject on Negative Impact (RONI) technique, which evaluates new data’s impact before it’s included in the training pipeline. As Microsoft researchers explain, "Machine Learning algorithms must be capable of discerning maliciously introduced data from benign ‘Black Swan’ events by rejecting training data with negative impact on results". This approach tests each data point’s influence on model behavior, filtering out inputs that could distort outcomes.
To strengthen defenses, deploy secondary monitoring models to detect gaps in primary systems and identify training/serving discrepancies before they influence production. Once data is validated, tracking its origins becomes critical to maintaining system integrity.
Data Provenance and Integrity Tracking
Tracing the origins and transformations of data ensures accountability and enables quick responses to issues. Lineage records metadata about datasets and their transformations, while provenance expands this to include metadata about the entire infrastructure and cryptographic verification of the supply chain.
"Lineage and provenance contribute to data management and model integrity, and forms the foundation for AI model governance."
- Google SAIF
Using cryptographic signatures, you can confirm that data sources remain uncompromised before ingestion. Tools like VAMP utilize cryptographic authentication and manifests to validate the integrity of datasets, software, and models. Additionally, proof-of-training-data protocols can verify which specific data points were used in training, leveraging overfitting tendencies to detect inclusion.
The level of tracking detail should align with system risk. For example, kernel-based system-call interception for provenance typically introduces only a 1% to 23% overhead, making it practical for critical sectors like finance or healthcare.
Encryption and Bias Detection Guardrails
After ensuring data quality and traceability, protecting data during transit and addressing bias are key steps to fortify the system. Data sanitization during preprocessing removes sensitive identifiers, preventing models from unintentionally revealing private data later. Signed attestations within trusted execution environments can further confirm that models have undergone proper testing before deployment.
To avoid model collapse, balance human-labeled data with model-generated data. For instance, maintaining a controlled ratio of human-to-model sample rates can mitigate bias amplification in generative models. A practical example of this is the 2020 PulseSatellite tool, which improved its Intersection over Union (IoU) scores from 0.62 to 0.87 by integrating human corrections into its retraining process, boosting completion rates by over 17 percentage points.
Explainable AI (XAI) offers transparency by auditing decisions and identifying biases. Additionally, adversarial training during development can simulate attacks, teaching models to recognize and counter deceptive inputs. Finally, maintaining hold-out datasets that are never reintroduced into the training loop provides a clean benchmark for ongoing evaluations.
How to Secure Feedback Loops
To create feedback loops that can adapt to threats without compromising efficiency, it’s crucial to weave security into every stage of the process. Let’s break down how to achieve this.
Strategy: Define Key Metrics and Goals
Start by translating your business goals into measurable security metrics. This means setting clear requirements for data privacy, preventing unauthorized access, and focusing defenses on risks like data poisoning, model inversion, and adversarial attacks.
Establish performance and security baselines. Alongside traditional metrics like accuracy and precision, include security-focused indicators such as "decision integrity" telemetry, which can identify shifts in training data quality. Add forensic capabilities to log classifier states, training timestamps, and key decision-making data – this ensures transparency and accountability.
These metrics form the backbone of secure, adaptive self-learning systems that can meet the demands of ongoing AI operations.
Build: Secure Data Ingestion and Processing
Once your metrics are in place, focus on securing the flow of data through your system.
Start at the entry point. Use validation checks and multiple data labelers to ensure accuracy before training begins. Tools like Microsoft Purview can track data provenance, creating a verifiable chain of custody and flagging "shadow datasets" that might bypass security protocols. Microsoft emphasizes the importance of training data stores in threat modeling.
To protect your data further, separate training data from production environments using tools like Managed VNets or Private Endpoints. Maintain dataset hashes and digital signatures, and enforce rigorous code reviews to prevent unauthorized changes. For highly sensitive workloads, consider hardware-based enclaves like Intel SGX or AMD SEV-SNP, which secure data during processing.
Additional techniques include applying differential privacy to reduce the impact of single poisoned records and using feature squeezing to detect adversarial examples by comparing predictions on original versus "squeezed" inputs. Always encrypt data at rest, enforce TLS for data in transit, and leverage hardware enclaves where necessary.
Deploy: Automate Testing and Controls
With data ingestion and processing secured, the next step is deploying automated controls to keep the feedback loop protected.
Incorporate adversarial examples into your evaluations to teach models how to respond defensively. Automate monitoring for data shifts and Out-of-Distribution inputs, and enforce frameworks like SLSA to verify artifact integrity. These measures help guard against vulnerabilities like data poisoning and adversarial attacks.
Set up event-driven remediation to instantly address security violations. This could include triggering rollbacks, applying patches, or activating kill switches. Use per-actor rate limiting (e.g., based on API keys or user IDs) to prevent large-scale model exfiltration. For instance, limiting queries to one per minute would stretch a 10,000-interaction attack to roughly 7 days, giving you ample time to detect and respond.
To further strengthen security, require dual reviews for all changes to minimize single-point failures. Deploy shadow models alongside production models to monitor for anomalies or malicious behavior without affecting live operations. Finally, integrate automated security scanning and digital signature verification directly into your CI/CD pipeline to detect and prevent vulnerabilities in model binaries.
Measuring Success and Maintaining Security
After setting up a feedback loop, the next logical step is to measure how well it works.
Tracking Metrics for Security and Compliance
Metrics are essential for gauging the effectiveness of your security measures. Start by examining operational efficiency: look at Mean Time to Respond (MTTR), investigation speed, and the extent of automation. These indicators reveal whether your feedback loop is cutting down on manual effort.
Pay close attention to accuracy metrics like false positive rates and correction rates. Feedback loops that quickly incorporate analyst corrections help maintain model precision. Also, track how fast these corrections are implemented – delays can erode transparency and trust.
To safeguard the system, regularly verify model and artifact integrity using version control and input validation. This helps prevent compromised data from infiltrating the loop. On the compliance side, ensure your metrics demonstrate that security controls align with your organization’s risk tolerance and provide insight into emerging threats.
These metrics lay the groundwork for making real-time adjustments, which is explored further in the next section on responding to evolving threats.
Adapting Feedback Loops Based on Threat Patterns
Threats are constantly changing, and your feedback loops need to keep pace. For instance, systems that retrain detection models weekly using self-labeled data have shown a dramatic reduction in jailbreak detection false negatives – from 4% to just 0.3%. This type of ongoing self-training allows the system to adapt to new attack patterns without requiring constant manual labeling.
Incremental fine-tuning is another effective strategy. It adjusts specific contextual parameters while leaving the base model weights unchanged. This approach works well alongside predefined performance thresholds, which can trigger necessary interventions. Instead of relying strictly on binary classifications, focus on monitoring specific behaviors, like how the system handles harmful prompts. For example, setting a performance threshold of 0.85 can automatically flag the need for manual review if that standard isn’t met.
Tools for Automation and Cost Efficiency
Automation not only simplifies compliance but also strengthens the security improvements achieved through effective feedback measurement. Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) platforms, such as OX Security, Apiiro, and ArmorCode, consolidate data from multiple scanners to give a unified view of your security posture. By 2026, it’s expected that 40% of organizations developing or acquiring applications will rely on ASPM platforms to manage their security frameworks.
For compliance, the Open Security Controls Assessment Language (OSCAL) offers a shift from manual processes to automated compliance monitoring. Leveraging OSCAL can cut audit times from months to just minutes. Additionally, integrating security scans into CI/CD pipelines – triggering scans automatically during pull request creation – provides immediate feedback to developers and helps catch vulnerabilities early.
| Tool Category | Examples | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| ASPM Platforms | OX Security, Apiiro, ArmorCode | Consolidates scanner data and prioritizes risks by business impact |
| Compliance Automation | OSCAL (NIST) | Automates audits, replacing manual documentation |
| Developer Feedback | AWS CodeGuru, Bandit, cfn-guard | Delivers real-time security insights during development |
| Endpoint Protection | Microsoft Defender for Endpoint | Blocks threats quickly across systems via shared signals |
Conclusion
Ensuring secure feedback loops in self-learning systems demands constant attention at every stage. As the RAND Corporation aptly highlights:
"AI security is not static – risks evolve throughout the lifecycle of your system, and adversaries exploit vulnerabilities at every phase." – RAND Corporation
This underscores the importance of implementing security measures from the very beginning, starting with data integrity during design, incorporating red-teaming in development, fortifying APIs during deployment, and maintaining vigilant runtime monitoring once the system is operational.
One of the key challenges lies in machine learning models’ inability to differentiate between harmful and harmless anomalies. Microsoft’s security team emphasizes this point:
"Machine Learning models are largely unable to discern between malicious input and benign anomalous data." – Microsoft Security Team
To address this, a multi-layered defense strategy is crucial. This includes tracking data provenance, using RONI (Reject-on-Negative-Impact) algorithms to filter harmful training samples, and employing real-time anomaly detection to identify and mitigate suspicious behavior as it occurs. Together, these practices help ensure the resilience of feedback loops against evolving threats.
However, securing AI systems involves more than just the models themselves. A comprehensive approach is necessary – one that safeguards APIs, data pipelines, and human interactions. Forensic tools, such as logs of classifier states, training timestamps, and decision metadata, play a vital role in maintaining both legal and ethical accountability. This holistic approach protects the entire system, reinforcing the robust mindset needed for secure AI operations.
Forward-thinking engineers must also assume the possibility of compromised training data or sources. This perspective drives the adoption of verifiable rewards, strict data lineage protocols, and frameworks like Audited Skill-Graph Self-Improvement (ASG-SI), ensuring that model updates are both transparent and auditable. The ultimate goal is to build resilient systems capable of detecting manipulation attempts while safeguarding sensitive information.
At TechVZero, we’ve witnessed how foundational security principles – such as robust access controls and continuous monitoring – can stop AI-specific attacks from becoming easily exploitable. True security isn’t about chasing buzzwords or flashy vendor claims. It’s about applying proven software security practices, focusing on measurable outcomes, and adapting as new threats emerge.
FAQs
How can I detect data poisoning early in a live feedback loop?
Detecting data poisoning early means keeping a close eye on your training data for anything unusual and validating new data through rigorous checks – like cross-referencing labels for accuracy. Tools like PCA-based models and other robust statistical methods can help identify inputs that don’t seem to fit. Additionally, anomaly detection tools are invaluable for flagging suspicious data.
Another effective approach? Ensemble learning. By training multiple models on different subsets of data, you create a system that’s much harder for attackers to compromise. This layered defense adds an extra barrier, making it tougher to exploit vulnerabilities.
What’s the simplest way to track data provenance end-to-end?
To keep track of data throughout its lifecycle, the easiest approach is to rely on automated systems that log metadata. These systems document details like where the data comes from, how it’s transformed, and where it moves, ensuring consistent traceability without requiring much manual work. Adding cryptographic methods, like hash functions, can further protect these records by making them tamper-proof. Together, these methods help establish a clear and reliable data lineage, which is crucial for meeting compliance standards, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring accountability in self-learning systems.
How do I stop feedback loops from amplifying bias over time?
To keep feedback loops in self-learning systems from amplifying bias, it’s important to use specific strategies. One key approach is relying on non-engagement signals to evaluate the quality of information, rather than just engagement metrics like clicks or likes. Another is carefully managing distribution shifts in the model’s outputs to avoid unintended patterns.
You can also simulate feedback effects using dynamical systems theory. This method helps uncover and address problems like popularity bias, where certain content gets overly promoted simply because it’s already popular.
Other critical steps include conducting regular bias assessments, creating synthetic datasets to reduce skewed patterns, and implementing bias-aware training methods. Together, these strategies can help minimize bias amplification in systems with continuous feedback loops.