Trigger Automated Tests in CI/CD Pipelines
Every time you push code, there’s a risk of introducing bugs or breaking functionality. Automated test triggers solve this by instantly running tests whenever changes occur in your codebase. These triggers ensure fast feedback, catch issues early, and improve team efficiency by automating repetitive checks.
Here’s what you need to know:
- What They Are: Automated test triggers start testing workflows based on events like code pushes, pull requests, or merges.
- Why They Matter: They reduce manual effort, speed up debugging, and ensure only tested code reaches production.
- Key Benefits:
- Immediate feedback to developers.
- Prevent regressions by validating every pull request.
- Save time by running only relevant tests (e.g., frontend for UI changes, backend for API updates).
- Choosing Tools: Popular CI/CD platforms like GitHub Actions and CircleCI offer robust support for automated testing, including parallelism, path filtering, and test reporting.
- Best Practices:
- Use triggers like push events, pull request updates, or scheduled jobs.
- Optimize pipelines with parallel execution, path filtering, and rerunning only failed tests.
- Maintain test reliability by addressing flaky tests and ensuring environment consistency.
Automated test triggers streamline your CI/CD process, saving time and ensuring higher code quality.
What Are Triggers In CI/CD Pipelines? – Next LVL Programming
Choosing the Right CI/CD Tools for Automated Testing
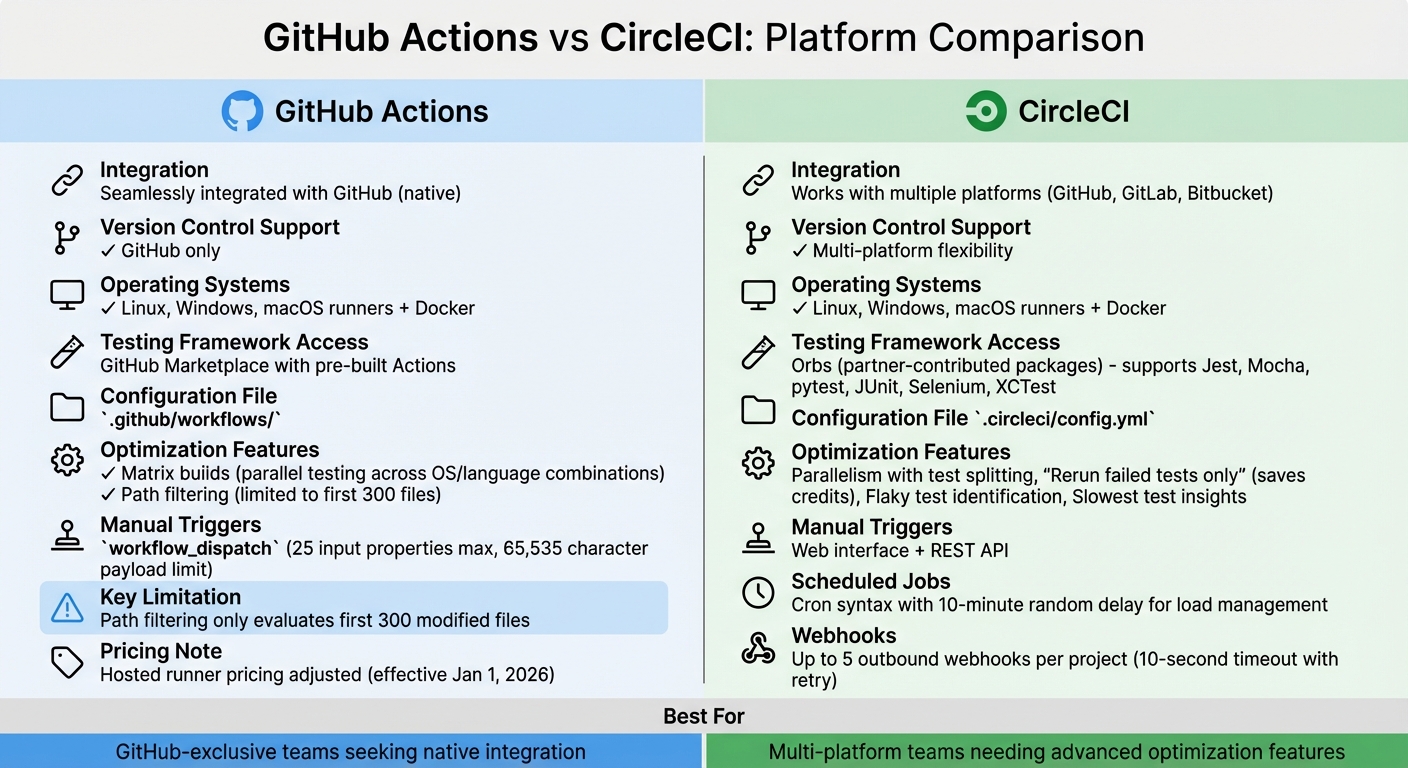
GitHub Actions vs CircleCI: CI/CD Platform Comparison for Automated Testing
Picking the right CI/CD platform is crucial for streamlining your development process. A poor choice can lead to inefficiencies, higher costs, and frustrated developers.
Common CI/CD Platforms for Automated Testing
GitHub Actions is seamlessly integrated with GitHub, making it an obvious choice if your codebase is already hosted there. It eliminates the need for external integrations or additional credentials. On the other hand, CircleCI works with GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, offering greater flexibility for teams using multiple version control systems. Both platforms support Linux, Windows, and macOS runners, as well as Docker-based environments.
When it comes to testing frameworks, CircleCI supports popular tools like Jest, Mocha, pytest, JUnit, Selenium, and XCTest. GitHub Actions provides similar functionality through its Marketplace, where you can find pre-built "Actions" for a wide range of testing tools. CircleCI uses "Orbs", which are partner-contributed packages that serve a similar purpose.
Key Factors When Selecting a Platform
Start with version control integration. If your team exclusively uses GitHub, GitHub Actions simplifies the process by removing the need for external authentication. For teams working across multiple platforms, CircleCI’s broader version control support can save time and effort.
Test framework compatibility is another critical consideration. Ensure your preferred testing tool is readily available in the platform’s ecosystem. For instance, if you rely on Cypress, LambdaTest, or Sauce Labs, having seamless integration is far better than writing custom scripts.
As your test suites grow, optimization features become indispensable. Look for capabilities like parallelism and test splitting, which distribute tests across multiple containers to reduce execution time. CircleCI offers a "Rerun failed tests only" feature, which conserves credits by skipping already-passed tests. GitHub Actions provides matrix builds, allowing tests to run across different operating systems and language combinations simultaneously.
Maintenance tools are also worth considering. CircleCI helps identify flaky tests and provides insights into the slowest ones. GitHub Actions recently adjusted its pricing for hosted runners, which could impact your budget starting January 1, 2026. Path filtering is another useful feature – it ensures that resource-intensive test suites only run when relevant code changes are detected. However, GitHub Actions limits path filtering to the first 300 files modified.
Initial Setup and Configuration
Most CI/CD platforms use YAML configuration files stored in your repository. For example, GitHub Actions uses .github/workflows/, while CircleCI relies on .circleci/config.yml. Many tools now offer "starter workflows" or templates that analyze your codebase and suggest configurations. For instance, they might recommend a Node.js template if they detect a JavaScript repository.
If your tests require specific hardware or operating system versions not provided by the platform, consider using self-hosted runners. This is especially important for teams with unique testing environments or strict security requirements that prevent using cloud infrastructure.
You might also need alternative triggers, such as REST APIs, scheduled cron jobs, or custom webhooks. GitHub Actions supports manual triggers via workflow_dispatch, which allows up to 25 top-level input properties and a payload limit of 65,535 characters.
Once your platform is set up, focus on fine-tuning your pipeline and optimizing test triggers for maximum efficiency.
Implementing Automated Test Triggers
When setting up your CI/CD pipeline, it’s essential to configure test triggers with well-defined stages and event rules. Once your platform is ready, organize the pipeline to ensure tests are triggered efficiently. A typical pipeline follows a Build → Test → Deploy flow, where each stage depends on the success of the previous one. For instance, tools like GitHub Actions (needs keyword) or CircleCI (workflows) can enforce this sequence. This setup not only saves resources but also provides quick, reliable feedback, helping to streamline the CI/CD process.
Structuring Pipeline Stages for Testing
Each pipeline stage should focus on a specific task. Here’s how to break it down:
- Build Stage: This step compiles your code and installs all necessary dependencies.
- Test Stage: Here, test suites are executed in isolated environments, such as Docker containers or platform-hosted runners.
- Deploy Stage: This stage runs only if both the build and test stages are successful.
For example, your test jobs should be explicitly configured to wait for the build jobs to complete. If your tests involve frequent Docker pulls, make sure to authenticate to avoid rate limits. And if your testing requires specific hardware or OS versions, self-hosted runners might be a better choice than relying solely on cloud-based infrastructure.
Setting Up Trigger Events
Triggers define when your pipeline starts running. The most common triggers include:
- Push Events: Run tests for every new commit.
- Pull Request Events: Validate code before merging by running tests on pull requests.
You can fine-tune these triggers by filtering branches (e.g., main or releases/**) or file paths to skip tests for non-code changes, like documentation updates. For pull requests, go beyond the "opened" event and include activities like "synchronize" or "reopened" to ensure tests run whenever needed. This approach avoids wasting CI credits.
Other options include scheduled triggers (using cron syntax) for tasks like nightly regression tests. CircleCI, for example, introduces a random delay of up to 10 minutes to manage system load effectively. Additionally, manual triggers – such as workflow_dispatch in GitHub Actions or using the CircleCI web interface – allow developers to run specific test suites on demand with custom parameters.
Note: GitHub Actions evaluates path filters on only the first 300 files in a diff. Once you’ve set up your trigger events, focus on optimizing how tests are executed.
Improving Test Execution Efficiency
Large test suites can slow down your pipeline, but there are ways to speed things up:
- Parallelism: Split tests across multiple containers to run simultaneously. Tools with built-in CLI features can distribute tests based on timing data, ensuring all parallel nodes finish around the same time.
- Path Filtering: Use this to trigger tests only when relevant files are changed, avoiding unnecessary runs.
- Matrix Builds: Run jobs across different OS versions, programming languages, or configurations. For example, you can test Node.js versions 18, 20, and 22 in parallel.
- Rerun Failed Tests Only: CircleCI offers this feature to save time and credits by skipping tests that previously passed.
Finally, tools like store_test_results can help capture and analyze test metrics. Regularly reviewing timing dashboards can uncover slow or flaky tests that need improvement. By addressing these bottlenecks, you can ensure your pipeline remains fast and efficient.
sbb-itb-f9e5962
Integrating Test Results and Enforcing Quality Gates
After setting up automated tests, the next logical step is to capture their output and use it to guide deployment decisions. Without integrating test results, teams are left manually combing through logs to determine if the code is production-ready. CI/CD platforms simplify this by collecting test data, enforcing quality standards, and notifying teams when issues arise. This builds on the automated test triggers configured earlier, ensuring a seamless workflow.
Setting Up Test Reporting and Artifacts
For CI/CD tools to process test results effectively, the data must follow a standardized format. JUnit XML has become a widely accepted standard, even outside Java projects. Many test runners either natively generate JUnit output or offer plugins to do so. For example, JavaScript projects can use jest-junit, Python projects can run pytest --junitxml, and Ruby developers can rely on rspec_junit_formatter.
CircleCI provides two key options for managing test data:
store_test_results: Displays pass/fail rates and timing metrics in the UI, giving teams a quick overview of their test performance.store_artifacts: Retains raw logs for deeper troubleshooting, useful for diagnosing flaky tests or performance issues.
Using both options strikes a balance between having quick insights for daily tasks and maintaining detailed records for complex investigations. However, keep in mind that storing artifacts may incur additional costs.
Standardized outputs like JUnit XML also unlock advanced features such as flaky test detection, intelligent test splitting, and timing dashboards. These insights help teams prioritize maintenance and streamline their CI/CD workflows.
Creating and Enforcing Quality Gates
Quality gates act as automated checkpoints that ensure only code meeting predefined standards moves forward in the pipeline. These gates can block deployments if certain criteria – like minimum code coverage (e.g., 80%), passing static analysis checks, or resolving critical security vulnerabilities – aren’t met. To maximize efficiency, quality gates should fail fast, halting the pipeline immediately when thresholds aren’t met.
While implementation varies by platform, the concept remains consistent. For instance:
- In GitHub Actions, you can use
continue-on-error: falseor includeexit 1in scripts to force job failures. - With SonarQube, enabling the
sonar.qualitygate.waitparameter ensures the pipeline pauses until quality analysis completes, with a default timeout of 300 seconds.
For custom requirements, shell scripts and tools like jq can help enforce standards. For example, you could parse a coverage JSON file, extract the percentage, and compare it to your target. If it falls short, the script exits with a non-zero status code, failing the build. This level of customization allows teams to define what “good enough” means for their projects.
Automated Feedback and Alerts
Once test results are collected, delivering immediate feedback is critical. Manual checks slow down issue resolution, so automating this step is key. Outbound webhooks can send real-time updates to tools like Slack, PagerDuty, or custom dashboards. For instance, CircleCI supports up to five outbound webhooks per project, sending events like workflow-completed or job-completed. If the receiving server doesn’t respond within 10 seconds, the system retries the delivery.
Beyond notifications, many platforms can directly comment on pull requests with details like test results, accessibility issues, or security scan findings. This helps reviewers identify quality concerns without leaving their workflow. For teams dealing with flaky tests, CircleCI’s Test Insights feature tracks historical success rates and execution times, making it easier to pinpoint problematic tests.
Integrating ChatOps tools, such as the CircleCI Slack orb, further streamlines communication. These integrations bring build statuses directly into team channels, where developers are already collaborating. Notifications for failed tests often include links to logs and artifacts, enabling quicker debugging. This real-time feedback loop ensures that issues are addressed promptly, keeping development on track.
Best Practices for Maintaining Effective Test Triggers
Setting up automated test triggers is just the beginning. Keeping them reliable as your codebase grows and your team expands is a whole different challenge. Over time, test suites can accumulate technical debt, leading to slower pipelines, false positives, and a general loss of trust in test results. When this happens, teams might start ignoring test outcomes, which defeats the entire purpose of automation.
Managing Flaky Tests and Test Maintenance
Automation isn’t a “set it and forget it” solution – test triggers need ongoing attention to stay dependable. One of the biggest risks to CI/CD reliability is flaky tests. These are tests that pass or fail inconsistently, even when no code changes have been made. Just one flaky test can undermine confidence in the entire test suite, potentially leading teams to revert to manual verification – negating the benefits of automation.
To combat this, many platforms use statistical models and automated reruns to identify whether a failure is caused by a random issue or a real bug. Once you’ve identified flaky tests, quarantine them. Move them to a separate suite so they don’t interfere with deployments or skew results. Some reporting tools even let you suppress flaky test failures – these tests still run for debugging purposes, but they won’t cause the entire build to fail.
Common causes of flaky tests include race conditions, poorly handled asynchronous operations, differences between local and CI environments, and shared global states between tests. Smart retry systems can help by analyzing error messages – if the messages vary between runs, the test is likely flaky; consistent errors usually point to an actual defect.
To fix flaky tests, make them atomic by focusing on one specific function. Use explicit dependencies instead of hidden assumptions, manage test data with fixtures or factory methods, and replace static "sleep" functions with callbacks or polling for asynchronous operations. Prioritize fixes based on the risk level, starting with tests that validate critical business workflows.
Ensuring Test Environment Consistency
Once flaky tests are under control, the next priority is maintaining a consistent test environment. Environment drift – when local and CI environments differ – can cause tests to pass locally but fail in CI, leading to frustrating debugging sessions and delays. The goal is to make your test environment as close to production as possible.
Using containers or virtual machines ensures that local development and CI/CD pipelines run in identical conditions. If dedicated test environments aren’t available, schedule regular resets to bring the environment back to its original state. This helps prevent issues like "stale data" from incomplete cleanups or caching problems.
Test data consistency is equally important. Always generate fresh, predictable data with fixtures instead of sharing database states across tests. For tests involving third-party systems, stub out those dependencies since you can’t control external environments, and they might introduce unnecessary flakiness.
Another often-overlooked factor is time zone awareness. Tests that rely on the current time or scheduled events can produce inconsistent results when run across different time zones. To avoid this, either account for time zone variations in your test design or use mocked time values to ensure consistent behavior.
Collaborating Across Teams for Better Results
Building effective test triggers isn’t just a technical challenge – it’s also a team effort. Developers, QA engineers, and operations teams need to work together. When these groups operate in silos, test suites can become bloated with redundant tests, critical scenarios might get missed, and no one feels responsible when something breaks.
For example, in 2025, a large enterprise worked with Veritis to overhaul its disjointed development workflow. By introducing a streamlined CI/CD pipeline that integrated source control and automated testing, the company saw 60% faster development cycles and a 30% reduction in build and release efforts. Standardizing workflows across teams reduced bugs and increased release frequency.
Involving all stakeholders early ensures that automation goals align with business priorities. Tools like Cucumber can facilitate Behavior-Driven Development (BDD), enabling tests to be written in plain language that even non-technical stakeholders can understand. This shared understanding ensures everyone knows what triggers a test and why it matters.
Clear communication is also key. Automated alerts via Slack or email should notify the right team members when builds fail, enabling quick action. Real-time dashboards and centralized logging replace manual reporting, offering cross-functional visibility into delivery performance. Teams can also collaboratively mark or unmark flaky tests, ensuring trust in the automated triggers.
Organizations that fully embrace CI/CD and foster strong cross-team collaboration report impressive results, including 50% faster code deployment and a 70% reduction in failures.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Automated test triggers transform manual roadblocks into streamlined quality checkpoints, delivering critical feedback in just minutes and enabling significantly faster, high-quality deployments.
Catching bugs during development isn’t just a time-saver – it’s a cost-saver too. Fixing issues in production can be up to ten times more expensive. By automating repetitive validation tasks, QA teams can redirect their energy toward exploratory testing and broader quality strategies.
To make the most of automated triggers, treat them as dynamic systems. Address pipeline failures immediately to maintain trust. Use path filtering to avoid unnecessary test runs and cut infrastructure costs. Parallel execution can also help trim test cycle times without sacrificing coverage.
"The most efficient automation testing is the kind you don’t have to think about." – MABL
Start with quick unit tests and save more resource-heavy end-to-end tests for later stages. Keep an eye on analytics to identify flaky or slow tests, and encourage collaboration across teams to ensure transparency and alignment. With integrated automation in place, you’re laying the groundwork for seamless, scalable continuous delivery.
FAQs
How do automated test triggers enhance the efficiency of CI/CD pipelines?
Automated test triggers make CI/CD workflows more efficient by kicking off builds automatically when certain events happen – like code pushes, pull requests, or scheduled tasks. This removes the need for manual steps, giving developers instant feedback on their code changes. That quick feedback helps catch and fix problems early, long before they make it to production. The result? Fewer delays and a codebase that’s always ready for deployment.
Triggers can be fine-tuned to focus on specific branches, tags, or file patterns, ensuring only the necessary tests run. This avoids wasting time and resources. Features like auto-canceling duplicate runs and setting up scheduled triggers add another layer of efficiency. These tools can speed up release cycles, lower costs, and make testing more reliable – all without requiring constant human input. According to TechVZero, integrating event-driven triggers into your CI/CD pipeline is a smart way to build faster and more cost-efficient workflows.
What should I consider when selecting a CI/CD platform for automated testing?
When selecting a CI/CD platform for automated testing, trigger flexibility should be a top priority. A reliable platform will let you set triggers for various events like code pushes, pull requests, scheduled tasks, or custom webhooks. This ensures your tests kick off automatically at the right times, eliminating the need for manual oversight.
Another key factor is integration with testing frameworks. Look for platforms that work seamlessly with tools like Jest, Mocha, pytest, or Selenium. Native support for these frameworks not only simplifies the setup process but often comes with built-in dashboards, making it easier to monitor test results and debug issues quickly.
Lastly, don’t forget about security and scalability. A strong platform will include features like role-based access controls and secure token management to safeguard your workflows. Depending on your team’s requirements, you might prefer cloud-hosted runners for easier scalability or self-hosted options for greater control. Striking the right balance between these elements will help you choose a platform that aligns with your workflow and budget.
How can teams ensure automated test triggers remain reliable over time?
To ensure automated test triggers remain dependable, teams should prioritize keeping configurations updated, secure, and aligned with current needs. One effective approach is storing trigger configurations in version control. This practice not only makes changes traceable but also ensures they undergo proper review.
Regularly reviewing trigger settings – like event filters and schedules – is equally important. This helps confirm they match the current state of the codebase. When it comes to API tokens, it’s essential to secure them by using secret managers, limiting their scope, and rotating them periodically to avoid authentication problems.
To optimize resource usage, consider enabling features such as auto-canceling outdated runs. Additionally, leverage monitoring tools to quickly spot flaky or failing tests. These steps can help maintain reliable and efficient CI/CD pipelines without requiring advanced infrastructure expertise.