Managing Secrets in Multi-Cloud Serverless

In serverless environments, managing secrets like API keys and database credentials is challenging due to their short-lived, stateless nature. When operating across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, the complexity increases with varying tools, IAM models, and pricing. Poor secrets management can lead to "secrets sprawl", increasing the risk of data breaches, which cost an average of $4.88 million per incident.
Key Takeaways:
- Challenges: Multi-cloud setups face configuration drift, inconsistent tools, and difficulty auditing secrets.
- Solutions: Use native tools like AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, or Google Secret Manager for integration, or cloud-agnostic tools like HashiCorp Vault and Doppler for centralized control.
- Best Practices: Automate secret rotation, enforce least privilege access, and monitor secret usage to reduce vulnerabilities.
Quick Comparison:
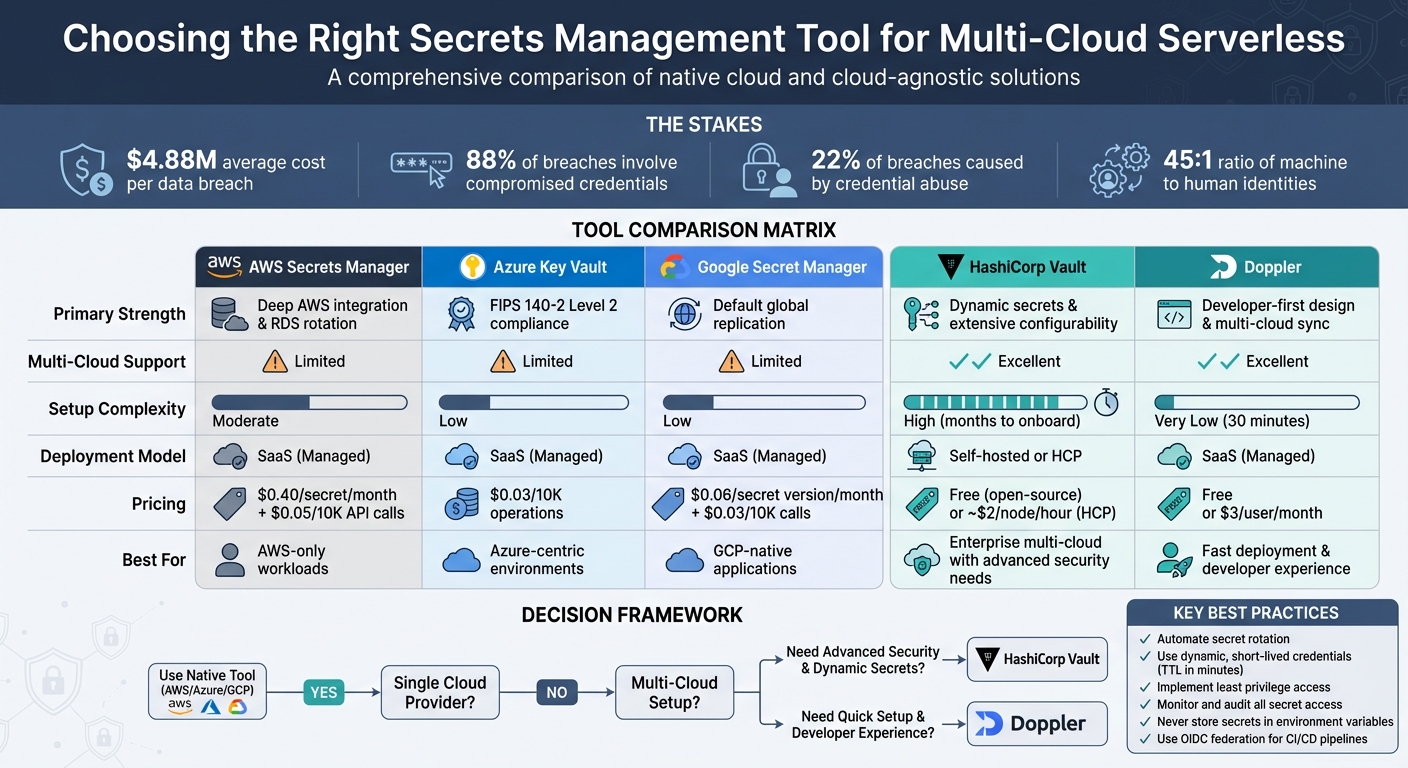
| Feature | AWS Secrets Manager | Azure Key Vault | Google Secret Manager | HashiCorp Vault | Doppler |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | AWS ecosystem integration | Centralized access | Global replication | Dynamic secrets | Developer-friendly |
| Multi-Cloud | Limited | Limited | Limited | Excellent | Excellent |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate | Low | Low | High | Very Low |
| Pricing | $0.40/secret/month | $0.03/10K operations | $0.06/secret version/month | Free or ~$2/node/hour | Free or $3/user/month |
To secure serverless applications, centralize secrets management, automate processes, and adopt short-lived credentials. The right tool depends on your cloud setup, scale, and security needs.
Multi-Cloud Secrets Management Tools Comparison: Native vs Cloud-Agnostic Solutions
Unlocking security harmony: Vault Secret Sync across multi-cloud environments
Native Cloud Secret Managers: Features and Use Cases
Major cloud providers offer built-in secret management tools designed to integrate seamlessly with serverless platforms. These tools – AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, and Google Cloud Secret Manager – help eliminate hard-coded credentials and simplify secret rotation. By understanding their features and limitations, you can determine whether these native tools meet your needs or if a more adaptable solution is required. Below, we dive into the specifics of each service and their integration benefits.
AWS Secrets Manager for Lambda
AWS Secrets Manager is designed to handle sensitive data like API keys, database credentials, and OAuth tokens. One standout feature is its ability to automatically rotate secrets without causing downtime or requiring code changes. For instance, if a Lambda function connects to Amazon RDS, Secrets Manager can rotate the database password every four hours without disrupting operations.
Integrating AWS Secrets Manager with Lambda is straightforward. Developers can retrieve secrets using the AWS SDK, the AWS Parameters and Secrets Lambda Extension (which provides a local HTTP interface on port 2773), or the Powertools for AWS Lambda parameters utility. The extension also caches up to 1,000 secrets for a default of 300 seconds, reducing both latency and costs by minimizing direct API requests.
Security is a core focus of AWS Secrets Manager. It uses AWS KMS for encryption and integrates with AWS CloudTrail to audit secret access events. Additionally, it supports cross-region replication, ensuring disaster recovery capabilities. Next, let’s explore Azure Key Vault and its integration with Azure Functions.
Azure Key Vault for Azure Functions
Azure Key Vault offers native integration with Azure Functions, working alongside Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Active Directory) for identity-based secret access. It centralizes the management of application secrets, cryptographic keys, and TLS/SSL certificates, providing a unified approach to securing sensitive data.
One of its key features is automated certificate enrollment and renewal from public certificate authorities, which is especially useful for Azure Functions managing HTTPS traffic. Access control is enforced through detailed IAM policies, ensuring that each function can only access the secrets it needs. This level of control also supports multi-cloud deployment strategies by reducing the risk of misconfigurations.
Google Cloud Secret Manager for Cloud Functions
Google Cloud Secret Manager integrates effortlessly with Cloud Functions, leveraging native IAM and Workload Identity to grant secret access without relying on long-lived service account keys. This eliminates the need to store static credentials in your function configuration, enhancing security.
The service includes secret versioning with rollback capabilities and automatic multi-region replication to ensure high availability. By default, all secrets are encrypted with AES-256, and users can opt for Customer-Managed Encryption Keys (CMEK) for additional control. While it doesn’t offer the same level of built-in automated rotation as AWS Secrets Manager, it excels in seamless runtime secret retrieval for Cloud Functions. This integration also supports multi-cloud strategies by helping prevent configuration drift.
Cloud-Agnostic Tools for Multi-Cloud Secrets Management
When working across multiple cloud platforms, relying solely on native secret managers can lead to inefficiencies and security gaps. Cloud-agnostic tools like HashiCorp Vault and Doppler offer a centralized way to manage credentials, eliminating the identity silos created by juggling multiple native tools. These solutions act as a unified hub for secrets, ensuring consistent security practices across different cloud environments.
Why Use Cloud-Agnostic Tools?
Cloud-agnostic tools provide flexibility by avoiding vendor lock-in, making it easier to shift workloads without requiring extensive code changes. They also simplify audits and consolidate credentials from various sources, such as CI/CD pipelines, containers, and cloud consoles. Centralizing secret management reduces the complexity of learning multiple APIs and workflows – a critical advantage considering that credential abuse accounts for 22% of data breaches.
HashiCorp Vault: Features and Use Cases
HashiCorp Vault is known for its ability to dynamically generate short-lived credentials for databases and cloud platforms, which automatically expire to minimize risks from leaked secrets. Take the example of Jannik Nolte, an IT Security Specialist at NORD/LB. By implementing Vault, his team automated key management, cutting down manual key rotation from three to four days per month to under five minutes.
Vault’s identity-based security model ensures that serverless functions only access the secrets they are authorized for, based on their authenticated identity. It also supports over 20 "Secret Engines" for interacting with sensitive data. One standout feature is the Transit Secrets Engine, which provides "Encryption as a Service." This allows serverless functions to encrypt and decrypt data without the need to handle raw encryption keys directly.
That said, Vault comes with a steep learning curve. Onboarding can take months and often requires dedicated resources to fully implement.
Doppler: Simplifying Secrets Management for Developers
Doppler prioritizes ease of use, making it a great option for smaller teams or those looking for quick deployment. Unlike Vault, Doppler can be set up in just 30 minutes. It eliminates the need for .env files and hardcoded secrets by using a CLI to inject secrets into both local development and production environments.
Doppler organizes secrets into Projects (representing applications or microservices) and Configs (like dev, staging, and production). It integrates with over 50 popular tools and services, and even syncs secrets automatically to native cloud managers like AWS Secrets Manager or Azure Key Vault. This streamlined approach makes it particularly appealing to serverless teams.
For production, Doppler uses Service Tokens to provide read-only access to specific configurations, ensuring least privilege access. Its activity logs and rollback features also make it easy to revert secret changes quickly if needed.
Comparing HashiCorp Vault and Doppler
Here’s a quick breakdown of how these tools differ and where they shine:
| Feature | HashiCorp Vault | Doppler |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Enterprise-scale security and flexibility | Developer experience and rapid setup |
| Deployment | Self-hosted, on-prem, or managed (HCP) | SaaS-only |
| Setup Time | Months to fully onboard | Around 30 minutes |
| Secret Types | Static, dynamic, encryption-as-a-service | Primarily static with orchestration |
| Learning Curve | Steep; requires dedicated resources | Low; intuitive and user-friendly |
Both tools bring unique strengths to the table, making them valuable for different use cases in multi-cloud strategies. Whether you’re an enterprise seeking robust security or a small team aiming for simplicity, there’s a solution to fit your needs.
sbb-itb-f9e5962
Best Practices for Secure Secrets Management in Multi-Cloud Serverless
After choosing your tools, it’s time to focus on keeping credentials secure across multiple cloud platforms. Credential abuse accounts for 22% of breaches, and machine identities now outnumber human identities by a staggering ratio of 45:1.
Automated Secret Rotation
Manually rotating secrets is time-consuming and prone to errors. Automating the process is far more efficient. Here’s how it works: generate a new secret, update the target service, test the new credential, and activate it. To avoid downtime, keep two secrets active until the rotation is confirmed.
Cloud-native secret managers simplify this process by using serverless functions – such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions – to handle secret rotation automatically. These functions can be triggered by schedules or specific events. However, the gold standard for security is adopting dynamic secrets. These are short-lived tokens with a time-to-live (TTL) measured in minutes. They’re generated on-demand and expire automatically. As Wiz aptly puts it:
"The most secure credential is one that doesn’t exist for long".
Different rotation strategies suit different needs. Time-based rotation (e.g., every 30 days) aligns well with compliance standards like PCI DSS or SOC 2. Event-driven rotation is ideal for responding to security breaches or policy violations. For zero-trust architectures, dynamic, on-demand secrets offer the highest level of protection. A key statistic: about 35% of exposed API keys remain active and vulnerable for extended periods after being leaked.
For CI/CD pipelines, consider using OIDC federation. For instance, GitHub Actions can exchange short-lived identity tokens for temporary cloud credentials, removing the need for static secrets in your pipeline configuration.
The next step? Tighten access controls.
Implementing Least Privilege Access
To minimize risks, assign unique IAM roles to each serverless function, limiting the scope of potential damage. Permissions should be as specific as possible – granting access only to the actions and resources required. For example, use secretsmanager:GetSecretValue instead of secretsmanager:*, and specify exact ARNs rather than using wildcards.
Breaking applications into smaller, isolated units of execution is another smart move. This ensures that if one function is compromised, the damage is contained. For example, a breach in a data processing function won’t affect authentication or payment functions. Additionally, separate production, staging, and development environments to ensure strict boundaries, so secrets aren’t shared across environments.
In multi-cloud setups, avoid long-lived credentials altogether. Instead, use OpenID Connect (OIDC) or native workload identities (like Microsoft Entra ID or Google Cloud Workload Identity) to exchange multi-cloud tokens for short-lived credentials in the target cloud. This approach works consistently across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. As NIST puts it:
"The principle that users and programs should only have the necessary privileges to complete their tasks".
Secrets should never be stored in environment variables or global variables, as this increases the risk of accidental exposure. Instead, fetch secrets directly from a secure vault at runtime. Limit function execution timeouts to the minimum necessary to reduce the window for exploitation.
While least privilege access reduces risk, monitoring ensures compliance and catches anomalies.
Auditing and Monitoring Secret Access
Centralized audit trails are critical for multi-cloud environments. A unified secrets management solution consolidates logs across cloud platforms, eliminating the need to manually gather logs from different systems. Log metadata like who accessed a secret, what action was taken, and when it occurred. However, ensure that actual secret values are never logged – automated redaction is essential.
Keep track of key lifecycle events: modifications, failed access attempts, secret rotations, and expiration dates. Set up alerts for unusual patterns, such as bulk secret retrievals, access from unexpected locations, or activity during off-hours. Notifications for failed authentication attempts or unauthorized access attempts can also help detect threats early.
A stark example of what can go wrong is the 2022 Uber breach. Attackers gained administrative access to all secrets because hard-coded credentials for a privileged access management tool were embedded in a PowerShell script. The attacker discovered and exploited this vulnerability. This highlights the importance of automated log redaction and scanning to prevent secrets from being exposed in application or build logs.
To further enhance security, use tools like AWS Zelkova to analyze resource policies and block overly broad or public access to secrets. Monitor how secrets are integrated into CI/CD pipelines, and leverage OIDC federation to avoid logging long-lived cloud access keys. As Jackson Connell from HashiCorp explains:
"Addressing sprawl with a secrets automation platform doesn’t just improve security, it unlocks engineering productivity at scale".
Comparison: Native vs. Cloud-Agnostic Secret Managers
Deciding between native cloud secret managers and cloud-agnostic tools largely depends on your system architecture and operational needs. Native options like AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, and Google Cloud Secret Manager shine when deeply integrated with their respective ecosystems. For instance, AWS Secrets Manager can rotate RDS credentials, while Google Cloud Secret Manager replicates secrets globally across all GCP regions by default. However, these tools often create platform-specific silos. For example, AWS Secrets Manager secrets are tied to specific regions, requiring manual replication for multi-region setups. This limitation often leads teams to explore centralized, multi-cloud alternatives.
Cloud-agnostic tools, such as HashiCorp Vault and Doppler, offer a unified approach to managing secrets across multiple providers. HashiCorp Vault supports dynamic secrets with configurable time-to-live (TTL) for over 50 systems. Meanwhile, Doppler focuses on simplicity and developer experience, offering a SaaS-only model that syncs secrets seamlessly to native managers.
Feature Comparison Table
Below is a breakdown of the key differences between native and cloud-agnostic secret managers:
| Feature | AWS Secrets Manager | Azure Key Vault | Google Secret Manager | HashiCorp Vault | Doppler |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Deep AWS integration & RDS rotation | FIPS 140-2 Level 2 compliance | Default global replication | Dynamic secrets & extensive configurability | Developer-first design & multi-cloud sync |
| Multi-Cloud | Limited (requires custom work) | Limited (Azure-focused) | Limited (GCP-focused) | Excellent (Cloud-agnostic) | Excellent (Universal sync) |
| Deployment | SaaS (Managed) | SaaS (Managed) | SaaS (Managed) | Self-hosted or Managed (HCP) | SaaS (Managed) |
| Scalability | Regional (manual replication needed) | High (Azure global infrastructure) | High (Global API support) | High (Horizontally scalable) | High (SaaS-based scalability) |
| Complexity | Low to Moderate | Low | Low | High (Requires expertise) | Very Low |
| Pricing | $0.40/secret/month + $0.05/10K API calls | $0.03/10K operations (Standard) | $0.06/secret version/month + $0.03/10K calls | Free (open-source); ~$2/node/hour (HCP) | Free Community plan; $3/user/month (Developer) |
When choosing a secret management solution, consider your operational priorities. If your workloads are entirely within one cloud provider, native managers offer seamless integration with built-in features like automated secret rotation and IAM support. For teams that value quick setup and a streamlined developer experience, Doppler is a strong choice, as it injects secrets as environment variables with minimal effort. On the other hand, HashiCorp Vault is ideal for enterprises needing advanced control, on-premises deployment, or complex dynamic credential generation.
Conclusion
Effectively managing secrets in multi-cloud serverless environments is no longer just an IT concern – it’s a critical business priority. With 88% of data breaches involving compromised credentials and the average breach costing a staggering $4.88 million, taking a proactive approach to secrets management is essential for safeguarding your operations, ensuring compliance, and improving reliability.
The key to success lies in moving away from scattered credentials and adopting centralized control planes that offer unified visibility and auditing. Depending on your needs, you might opt for native tools like AWS Secrets Manager, which integrate seamlessly into specific ecosystems, or multi-cloud platforms like HashiCorp Vault, designed for broader orchestration. Whichever you choose, the decision should align with your architecture and operational goals. Centralizing secrets management not only enhances security but also strengthens governance and auditing processes.
"There’s no way to build solid governance, auditing, and security around organizational access to secrets if you don’t centralize your management through one control plane." – HashiCorp
This unified approach directly addresses the multi-cloud challenges we’ve explored. Choosing the right tool – whether native or cloud-agnostic – is a crucial step in mitigating the risks outlined earlier.
Transitioning from static credentials to dynamic, short-lived secrets offers a significant security advantage. Features like automated rotation (as frequent as every four hours with AWS Secrets Manager), implementing least privilege at the function level, and using client-side caching for cost efficiency are key practices. Together, these form the backbone of secure serverless operations.
In serverless architectures, every function represents its own security perimeter. The tools and strategies you adopt today will determine whether your multi-cloud infrastructure becomes a competitive strength or a compliance liability.
FAQs
What should I consider when choosing a secrets management tool for a multi-cloud serverless environment?
When choosing a secrets management tool for a multi-cloud serverless environment, start by ensuring it provides centralized management. This allows you to securely store, rotate, and audit secrets from one place, simplifying the process of handling multiple cloud providers. It’s also crucial to have native multi-cloud support, meaning the tool should work effortlessly with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud without needing extensive custom setups.
Security features like dynamic secret generation (credentials that automatically expire) and fine-grained access control are key to reducing risks. Additionally, look for seamless integration with serverless runtimes, such as AWS Lambda and Azure Functions, as well as CI/CD pipelines. This can help prevent accidental exposure of secrets during deployments. Don’t overlook the cost and operational demands – SaaS solutions often provide predictable subscription pricing, while self-hosted options may offer greater control but require more effort to manage infrastructure.
To make an informed choice, consider running a small proof-of-concept. For example, test storing and accessing API keys across your serverless services to evaluate the tool’s performance, usability, and overall cost. TechVZero can assist in identifying the right tool that balances security, efficiency, and budget for your specific requirements.
Why should I use cloud-agnostic tools instead of native secret managers?
Cloud-agnostic secret management tools offer a streamlined way to handle secrets across diverse environments, including AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and even on-premises setups. By using a single API and interface, teams can simplify essential tasks like secret rotation, audit logging, and role-based access control. This eliminates the need to master different tools for each platform, cutting down on complexity, operational burden, and the chances of misconfigurations.
Another major advantage is avoiding vendor lock-in. With a cloud-agnostic approach, migrating workloads or adopting new cloud providers becomes much simpler, as there’s no need to overhaul your secret management strategy. Centralized oversight and shared policies also help maintain consistent security practices, make compliance easier, and speed up response times during incidents.
On top of that, these tools can reduce costs and effort by integrating seamlessly with existing infrastructure, such as Terraform, while removing the need for multiple SDKs or specialized training. This leads to a more efficient and scalable workflow, especially as your multi-cloud setup expands.
Why is automated secret rotation important in serverless environments?
Automating secret rotation is a key practice in serverless environments. By routinely updating sensitive credentials, it reduces the chances of attackers exploiting leaked or outdated secrets.
Beyond tightening security, automated rotation helps align with industry standards and prevents service interruptions that could occur from expired or compromised keys. It’s a smart approach to keeping systems secure and dependable, especially in fast-changing, multi-cloud setups.