How AI Reduces Kubernetes Overprovisioning Costs

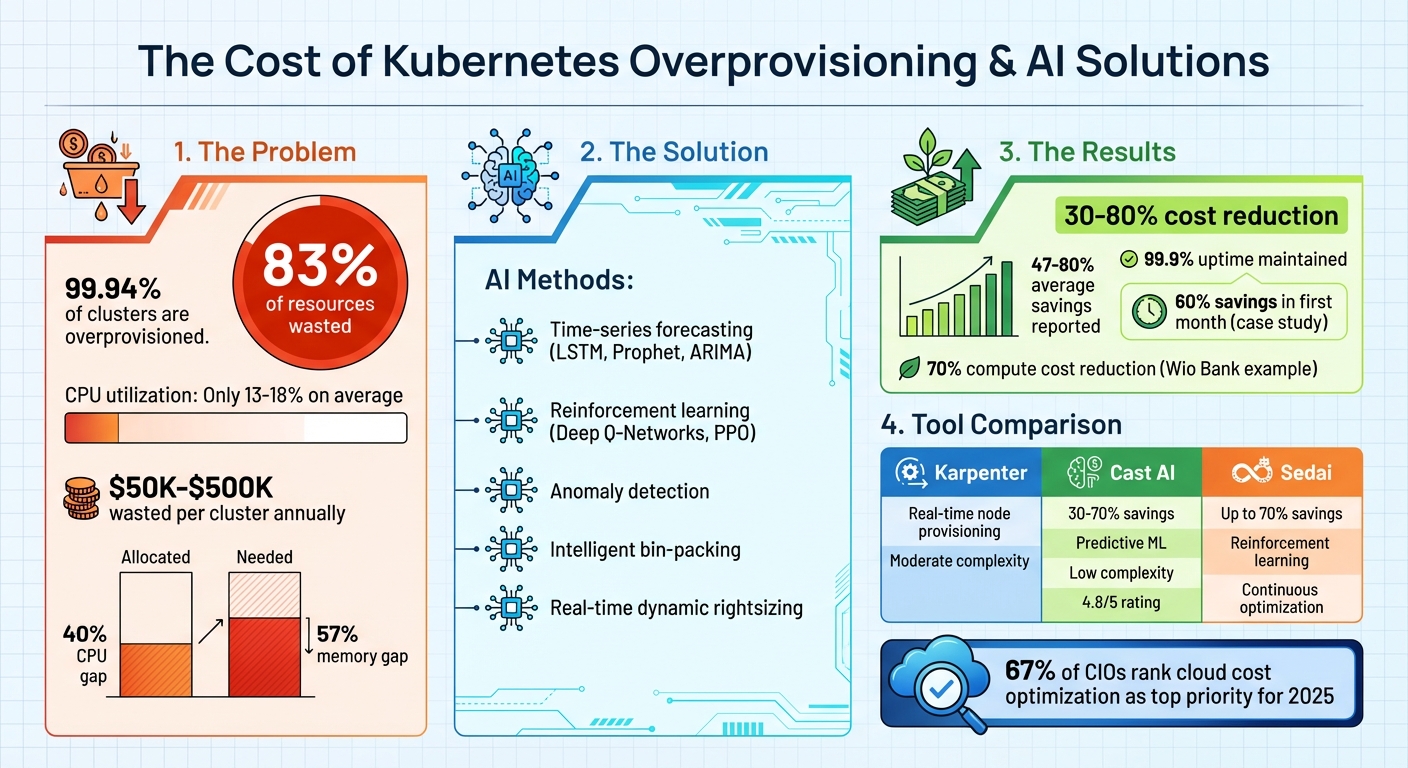
Overprovisioning in Kubernetes wastes up to 83% of resources, costing companies thousands annually. AI tools can slash these costs by up to 80%.
Overprovisioning happens when Kubernetes allocates more resources (CPU, memory) than workloads actually use. This common issue stems from conservative safety margins, poor visibility into resource usage, and planning for rare traffic spikes. The result? Companies pay for unused capacity, with some wasting $50,000–$500,000 per cluster annually.
AI-driven solutions fix this by predicting resource needs, optimizing workloads, and dynamically adjusting allocations. Tools like Cast AI, Karpenter, and Sedai use techniques like machine learning, intelligent bin-packing, and real-time scaling to reduce waste. For example, Cast AI users report savings of 30-70%, while Sedai helps companies like Wio Bank cut compute costs by up to 70%.
Key Takeaways:
- Why it matters: Overprovisioning leads to massive cloud waste, with CPU utilization averaging just 13%.
- AI’s role: Predictive scaling, workload rightsizing, and smarter scheduling reduce inefficiencies.
- Proven results: Companies save tens to hundreds of thousands annually using AI tools.
Want to cut Kubernetes costs? Start by monitoring resource usage, then deploy AI tools for dynamic optimization.
AI-Driven Kubernetes Cost Optimization: Key Statistics and Savings
Problems with Kubernetes Default Scheduling
Static Scheduling Creates Resource Waste
Kubernetes’ default scheduling approach often leads to inefficient resource usage, particularly in overprovisioned clusters. The default kube-scheduler prioritizes speed and availability, using a "LeastAllocated" strategy to distribute pods across as many nodes as possible. While this ensures load balancing, it also results in clusters where many nodes operate at just 20–40% utilization. Instead of consolidating workloads onto fewer nodes, this approach leaves clusters with excess, unused capacity.
A key issue lies in how Kubernetes handles resource requests. When you define static resource requests in YAML manifests, Kubernetes reserves the full amount specified, regardless of whether the pod actually uses that much. This reserved capacity remains locked, unavailable for other pods, leading to significant inefficiencies. Shockingly, 99.94% of Kubernetes clusters are overprovisioned, with an average gap of 40% for CPU and 57% for memory between what’s allocated and what’s truly needed.
Adding to the inefficiency is the "bin-packing" problem. Optimal pod placement is a computationally complex task, so the default scheduler relies on lightweight heuristics for quick decisions. These simplified strategies often result in fragmented resources. For example, a node might have 2 free CPU cores but lack the memory required to host an additional pod. This fragmentation and reliance on static scheduling make it difficult to fully utilize available resources, creating challenges when workloads fluctuate.
Handling Changing Workloads
Dynamic workloads introduce even more complexity. Modern applications often have unpredictable resource demands, but Kubernetes keeps resource allocations fixed once a pod is assigned to a node – unless the pod is restarted. This rigidity forces autoscalers to plan for peak usage, leaving up to 83% of compute resources underutilized during periods of lower demand.
Autoscalers themselves face limitations. Both the Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) and Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) rely on historical or reactive metrics rather than predicting future needs. This approach often triggers pod restarts and can lead to inefficient scaling decisions. For instance, restarting pods can cause cold starts in Java applications or result in cache losses for systems like Redis.
"The scheduler only sees resource requests, not actual usage." – DevZero
This disconnect between requested and actual resource usage further compounds the inefficiencies, making it challenging for Kubernetes to adapt to the dynamic nature of modern workloads effectively.
sbb-itb-f9e5962
How AI Improves Kubernetes Scheduling
AI Methods for Resource Optimization
AI is reshaping how Kubernetes handles scheduling, turning it into a predictive, intelligent process. Time-series forecasting models – like LSTMs, Prophet, ARIMA, and XGBoost – analyze historical traffic trends to predict future resource needs. This means your cluster can scale up before a morning traffic surge, keeping performance smooth.
Using reinforcement learning, Kubernetes can go a step further. Techniques such as Deep Q-Networks and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) learn from real-world feedback, fine-tuning scaling policies and selecting instances based on what works best in your specific environment. Anomaly detection also plays a key role, spotting unusual workload spikes early so resources can be adjusted proactively – avoiding performance dips.
Pod placement becomes more efficient with intelligent bin-packing algorithms, which replace Kubernetes’ default "spread everything everywhere" approach. Tools like Cast AI’s Pod Pinner ensure pods are packed strategically, reducing the number of active nodes and cutting costs. For even greater efficiency, CRIU-driven live migration allows running applications to move between nodes without service interruptions, preserving memory states and TCP connections.
AI also enables real-time dynamic rightsizing, which continuously adjusts CPU and memory allocations without downtime. This eliminates the need for overprovisioning safety buffers. By analyzing CPU, memory, network, and I/O usage, AI ensures resources are right-sized dynamically. Some platforms even incorporate multi-metric decision-making, factoring in application-specific signals like queue depth, request latency, and database queries – going beyond basic CPU and memory thresholds. These smarter adjustments lead to lower costs and higher efficiency.
Benefits of AI-Driven Scheduling
The impact of these AI techniques is both financial and operational. AI-driven resource optimization can cut Kubernetes workload costs by up to 80%, with most organizations seeing savings between 30-50%. For example, one company slashed daily expenses by 30% within just 24 hours, ultimately reducing costs by 60% within a month. These are game-changing results, not minor tweaks.
AI also drastically improves resource utilization. Consider the average CPU utilization in enterprise clusters – just 18%. AI-driven scheduling can push that number much higher by eliminating inefficiencies built into Kubernetes’ default behavior. Companies using predictive scaling techniques report uptime as high as 99.9%, as AI anticipates traffic and scales resources accordingly.
"By shifting from reactive to proactive scaling, AI reduces costs, enhances performance, and ensures reliability." – Sarthak Arora
Operationally, AI simplifies Kubernetes management. Instead of constantly monitoring and manually tweaking resources, teams can focus on innovation and building new features. This is critical, especially as 67% of CIOs rank cloud cost optimization as a top priority for 2025. By addressing overprovisioning and inefficiencies, AI-driven scheduling transforms Kubernetes from a resource-heavy system into a streamlined, cost-effective solution.
This Tool Will Help You Cut Down Your Kubernetes Cost by Up to 90%
AI Tools That Reduce Overprovisioning Costs
When it comes to cutting down overprovisioning costs, AI tools offer practical solutions with real-world applications. Let’s dive into how three standout tools – Karpenter, Cast AI, and Sedai – tackle this challenge.
Karpenter: Real-Time Node Provisioning

Karpenter simplifies node provisioning by monitoring unscheduled pods and deploying cost-efficient compute options in real time. Instead of relying on static node groups, it evaluates resource requests and selects from hundreds of instance types to find the best fit. This flexibility makes it ideal for workloads with constantly changing demands.
Using a single declarative NodePool resource, Karpenter also offers a NodeOverlays feature (currently in alpha) for teams with custom pricing agreements or Savings Plans. This ensures scheduling decisions align with your actual costs, not just public rates. However, it’s worth noting that Karpenter optimizes nodes based on pod requests, not actual usage, so it doesn’t address inefficiencies at the workload level. By focusing on intelligent node selection, it helps reduce wasted capacity and lowers cloud expenses.
Cast AI: Intelligent Autoscaling
Cast AI goes a step further by optimizing both workloads and nodes. Its predictive model, trained on millions of workloads, adjusts CPU and memory requests down to the millicore level to align with actual usage. This is crucial given that most Kubernetes applications use only a fraction of their allocated resources – just 10% of CPU and 23% of memory.
The platform can scale clusters rapidly, going from zero to 2,000 CPUs in under two minutes to handle traffic surges. It also predicts interruptions 30 minutes in advance, allowing seamless workload migration before any disruption occurs.
"Reducing 40% of our compute costs just by migrating our workloads to Cast AI – that’s huge."
- Achi Solomon, Director of DevOps, Yotpo
Akamai’s Senior Director of Engineering, Dekel Shavit, reported savings of 40-70% after implementing Cast AI. The tool can be deployed in a read-only mode initially, letting teams assess potential savings before making changes. It also integrates seamlessly with Karpenter, adding advanced workload management without disrupting existing setups. With over 2,100 companies using it and a 4.8/5 rating from more than 50 reviews, Cast AI has become a trusted choice for automated optimization.
Sedai: Continuous Optimization
Sedai takes a long-term approach, using reinforcement learning to optimize Kubernetes environments. It focuses on node rebalancing and defragmentation to enhance cost efficiency over time. By learning your application’s infrastructure needs and predicting traffic patterns, Sedai fine-tunes provisioning decisions. It can even work alongside Karpenter, recommending ideal memory-to-CPU ratios and sending updates for better node selection.
The platform also evaluates workloads for spot-friendliness, automatically switching between spot and on-demand instances as needed. Wio Bank achieved up to 70% savings on compute resources using Sedai’s AI-driven automation. By balancing cost, performance, and availability, Sedai ensures sustained reductions in inefficiencies.
Tool Comparison
Here’s a quick comparison of how these tools address overprovisioning:
| Tool | AI Method | Cost Savings Claimed | Integration Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Karpenter | Scheduling simulation for real-time node provisioning | Significant savings with dynamic workloads; requires NodeOverlays for custom pricing | Moderate (native Kubernetes CRDs) |
| Cast AI | Predictive ML for workload rightsizing and forecasting interruptions | 30-70% savings; up to 93% utilization improvements | Low (read-only mode available; agent-based deployment) |
| Sedai | Reinforcement learning for continuous optimization | Up to 70% sustained savings reported | Moderate (agent-based; works with existing tools) |
Each tool offers unique strengths. Karpenter shines in real-time node provisioning, Cast AI combines workload and node optimization with enterprise-ready features, and Sedai focuses on continuous learning and long-term efficiency. The right choice depends on whether you need immediate node provisioning, comprehensive automation, or a solution that adapts to evolving application behavior.
How to Implement AI-Powered Cost Reduction
You don’t need to overhaul your entire infrastructure to start cutting costs with AI. Instead, focus on understanding where you’re wasting resources, use the right tools to address inefficiencies, and make smart decisions about your infrastructure for long-term savings.
Monitor Current Resource Usage
Before diving into AI tools, you need a clear view of how your resources are currently being used. Start by deploying Prometheus to collect time-series data and install Node Exporter on all hosts to expose system metrics. Configure Prometheus to scrape data from your endpoints and connect it to Grafana to visualize key metrics like CPU saturation, memory usage, and disk I/O. Break down your data by cluster, namespace, and workload to pinpoint waste. For example, calculate wasted resources using this formula: Requested – Used = Wasted.
Here’s a staggering fact: in clusters with 50 CPUs or more, only 13% of provisioned CPUs are typically used. Even in setups with over 1,000 CPUs, utilization only climbs to 17%. To track normalized costs, use PromQL’s rate() function over five-minute intervals, dividing total compute costs by total provisioned CPUs. Tools like Cast AI can give near real-time insights, refreshing cost and resource data every 60 seconds and syncing cluster state changes every 15 seconds.
Deploy AI-Based Scheduling Tools
Once you understand your resource usage, the next step is deploying AI-based tools to fix inefficiencies. Start with a read-only agent or an agentless "Cloud Connect" method to scan your clusters and generate savings reports without disrupting operations. This helps you identify cost-saving opportunities while keeping your infrastructure intact.
After identifying waste, enable workload rightsizing to adjust CPU and memory requests based on actual usage patterns. This ensures you’re not over-allocating resources, a common issue.
"Phlexglobal saved 60% on cloud expenses by implementing automated instance selection and rightsizing in 2025; their VP of Cloud Engineering explained that the solution acts autonomously by purchasing resources according to specifications, simplifying engineers’ workflows."
Next, implement automated bin-packing to consolidate workloads onto fewer nodes, shutting down idle ones. For instance, Flowcore cut cloud waste by 50% using this method. Combine this with continuous automated rebalancing to replace inefficient nodes with more cost-effective options. Wio Bank saw savings of up to 70% by using this approach.
For teams running Karpenter, AI tools can enhance workload rightsizing and improve Spot instance reliability without disrupting existing NodePool setups. Configure Spot fallback to automatically switch to On-Demand instances during capacity shortages, reverting back to Spot when availability improves. Advanced interruption prediction can also provide alerts up to 30 minutes before a node becomes unstable – far better than AWS’s standard two-minute warning.
Consider Bare Metal Infrastructure
Cloud providers make scaling simple, but convenience comes at a price. Shifting to bare metal Kubernetes can slash costs by 40–60% while maintaining reliability comparable to managed cloud services [TechVZero]. Partner with specialists to handle the complexities of bare metal and take advantage of the savings. For example, TechVZero operates on a performance-based model: you pay 25% of the savings for a year, and nothing if they don’t hit their target. They’ve saved clients $333,000 in one month while also mitigating a DDoS attack [TechVZero].
For smaller teams (10–50 engineers), this approach offers compliance with standards like SOC2, HIPAA, and ISO without lengthy setup times. After optimizing workloads with AI-driven scheduling, transitioning to bare metal aligns your capacity with demand even more precisely, creating a compounding effect that maximizes your savings.
Conclusion
Key Benefits of AI for Kubernetes Cost Savings
AI-driven scheduling addresses one of Kubernetes’ biggest inefficiencies: unused compute resources. Research reveals that as much as 83% of provisioned compute capacity often sits idle. While traditional autoscalers depend on historical data and require disruptive restarts, AI tools use predictive analytics to anticipate demand and adjust resources dynamically – no downtime required.
The financial advantages are hard to ignore. Companies that have implemented AI-powered optimization report cost reductions between 47% and 80%. But the benefits go beyond just saving money. These tools also remove the need for constant manual adjustments. As Alex Potter-Dixon, VP of Cloud Engineering at Phlexglobal, described:
"With Cast AI, it’s essentially simply an annotation, and then the solution will act autonomously, purchasing more resources in accordance with our specifications. This simplifies the lives of our engineers."
AI automation further resolves scalability issues by freeing engineering teams from the tedious cycle of manual resource management, often referred to as "optimization debt." This allows them to focus on innovation and building new features. By eliminating overprovisioning waste, AI transforms Kubernetes from a cost liability into a strategic advantage.
Next Steps
Start by analyzing your current resource usage to pinpoint areas of overprovisioning. Once you’ve identified inefficiencies, test AI-based scheduling in a non-production environment. Prioritize features like automated rightsizing, intelligent bin-packing, and spot instance management to achieve immediate gains. For even greater savings, consider whether migrating certain workloads to bare metal Kubernetes can cut out hypervisor overhead and cloud provider markups. Use these insights to roll out AI scheduling tools and explore options like TechVZero to maximize cost efficiency.
FAQs
How can I tell if my Kubernetes cluster is overprovisioned?
To spot overprovisioning, keep an eye on resource utilization and compare it against the set requests and limits. In many clusters, memory requests are often 3–8 times higher than the actual usage. Similarly, CPU utilization typically hovers around 12–18%. These trends point to considerable overprovisioning, leading to wasted resources.
Will AI cost optimization hurt latency or reliability during traffic spikes?
AI-powered cost management in Kubernetes helps cut expenses while keeping latency and reliability intact, even during traffic surges. By fine-tuning resource allocation and adjusting scaling dynamically to match workload needs, it ensures top-notch performance and consistent service quality.
What’s the safest way to roll out AI-driven rightsizing in production?
To ensure a secure and efficient system, the best strategy is to adopt automated workload rightsizing with continuous monitoring. This involves leveraging algorithms that assess both real-time and historical data to fine-tune resource allocation. By making adjustments on the fly, you can keep the system running smoothly with zero downtime, even as it adapts to shifting demands.